Research Archive
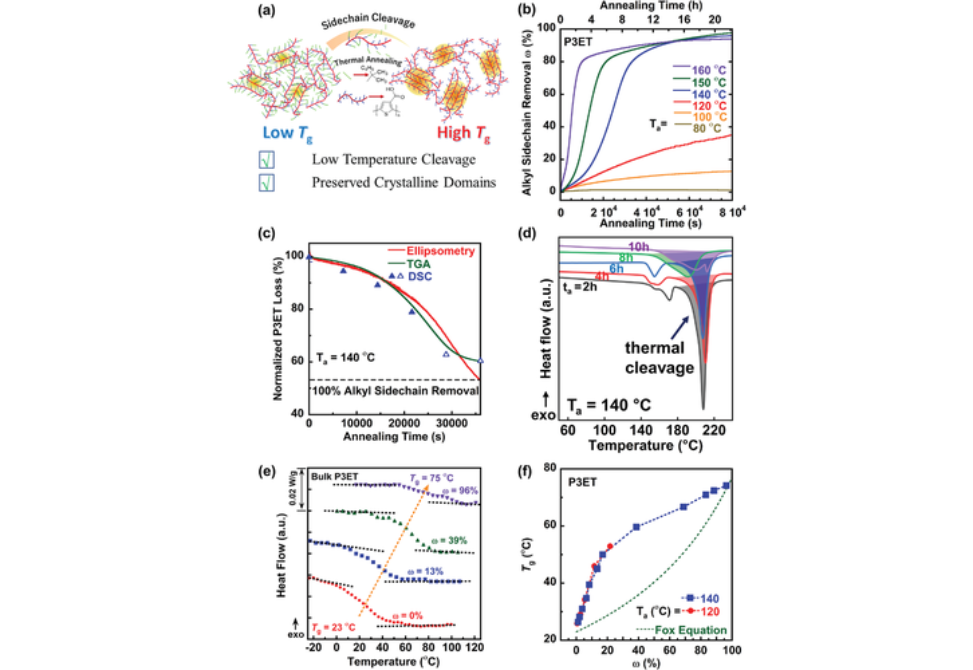
In this work, the Tgs for CPs are systematically studied with controlled side chain cleavage.
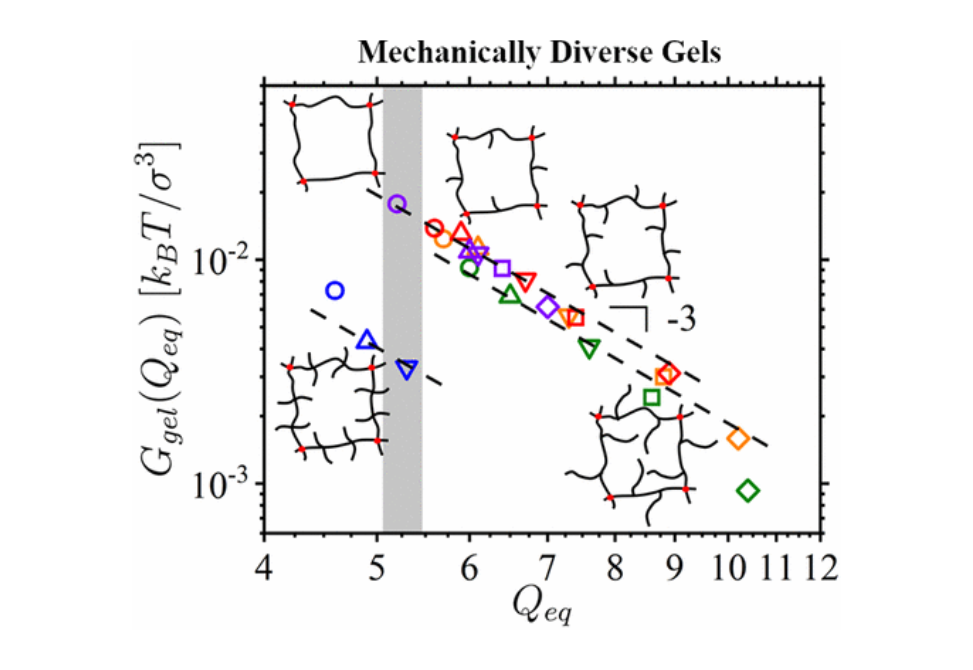
We use a combination of the Flory–Rehner approach, scaling analysis, molecular dynamics simulations, and experimental data for poly(n-butyl acrylate) (PBA) networks swollen in toluene to elucidate the effect of brush strand architecture on the equilibrium swelling ratio, Qeq, the modulus of the swollen gel, Ggel(Qeq), and its relationship with the nonlinear modulus of the dry network, G(Qeq)
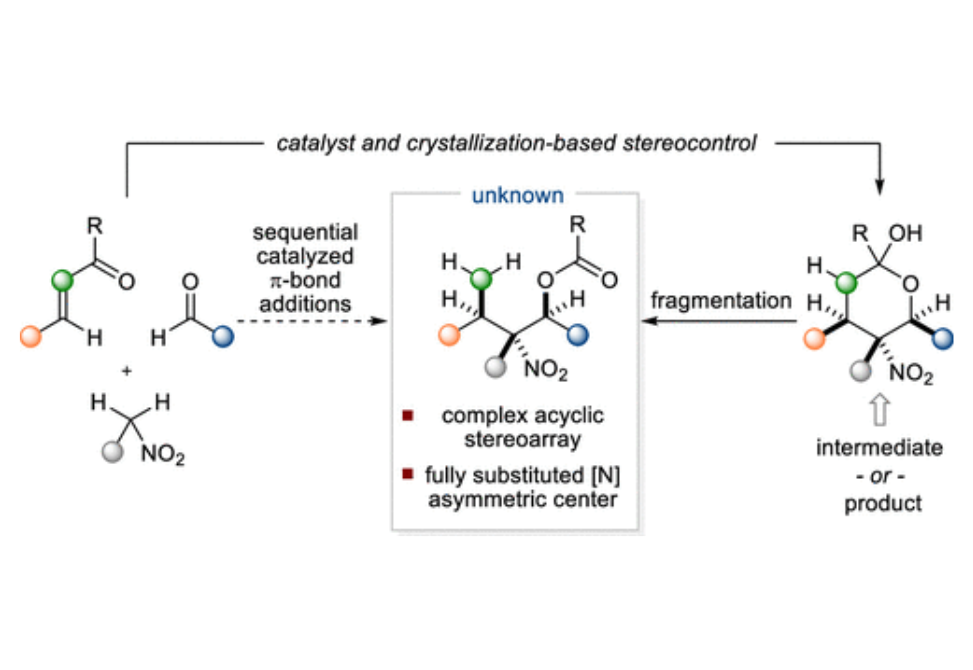
This article describes stereoconvergent Henry reactions of γ,γ-disubstituted nitroalkanes to deliver highly functionalized building blocks containing up to five contiguous stereogenic centers including a fully substituted [N]-asymmetric center.
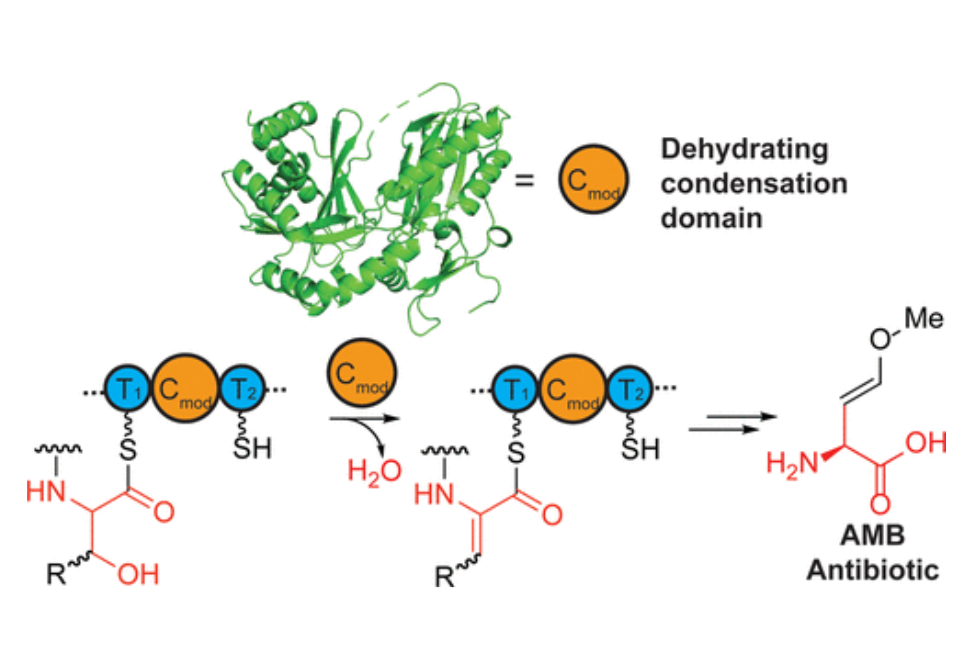
Here, we provide biochemical and bioinformatic evidence in support of the role of a unique class of condensation domains in dehydration (CmodAA).
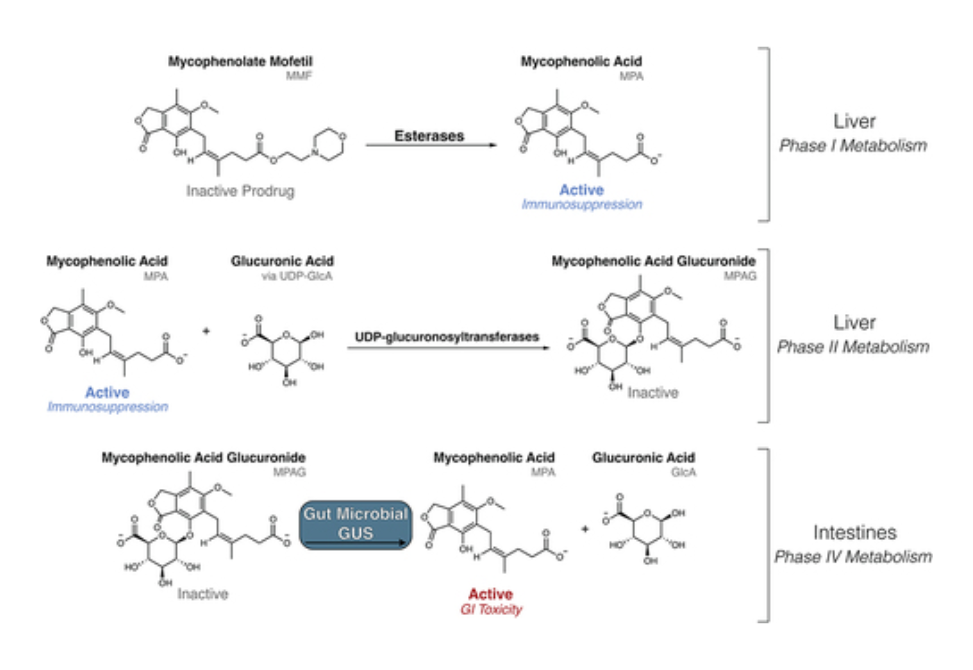
Here, we compare the fecal microbiomes of transplant recipients receiving MMF to healthy individuals using shotgun metagenomic sequencing.
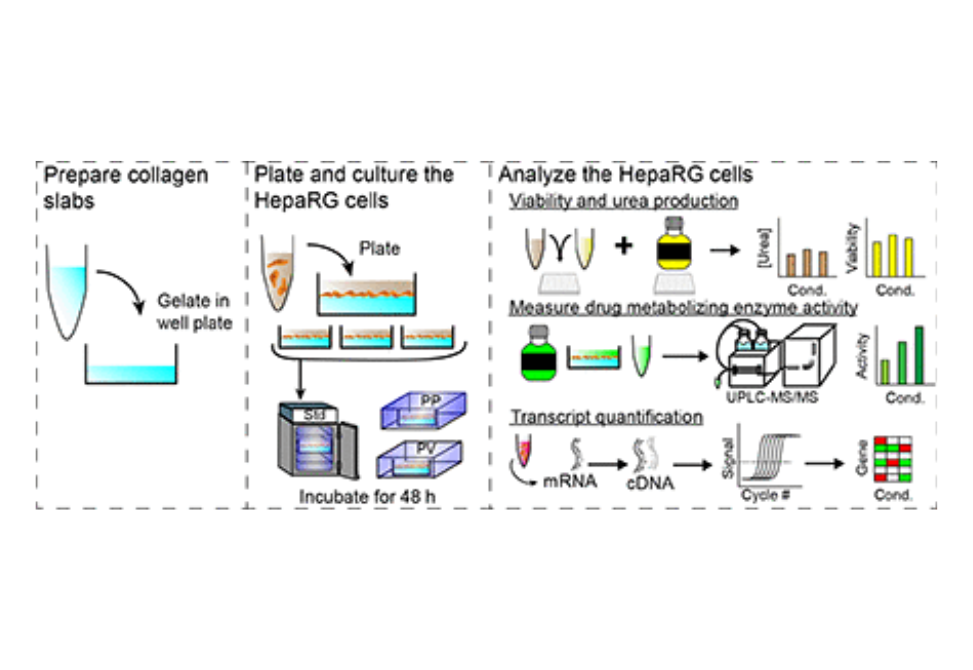
We hypothesized that incorporating physiologically relevant environments would promote post-differentiation patterning of hepatocytes and result in zonal-like characteristics. To test this hypothesis, we evaluated the transcriptional regulation and activity of drug-metabolizing enzymes in HepaRG cells exposed to three different oxygen tensions, in the presence or absence of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
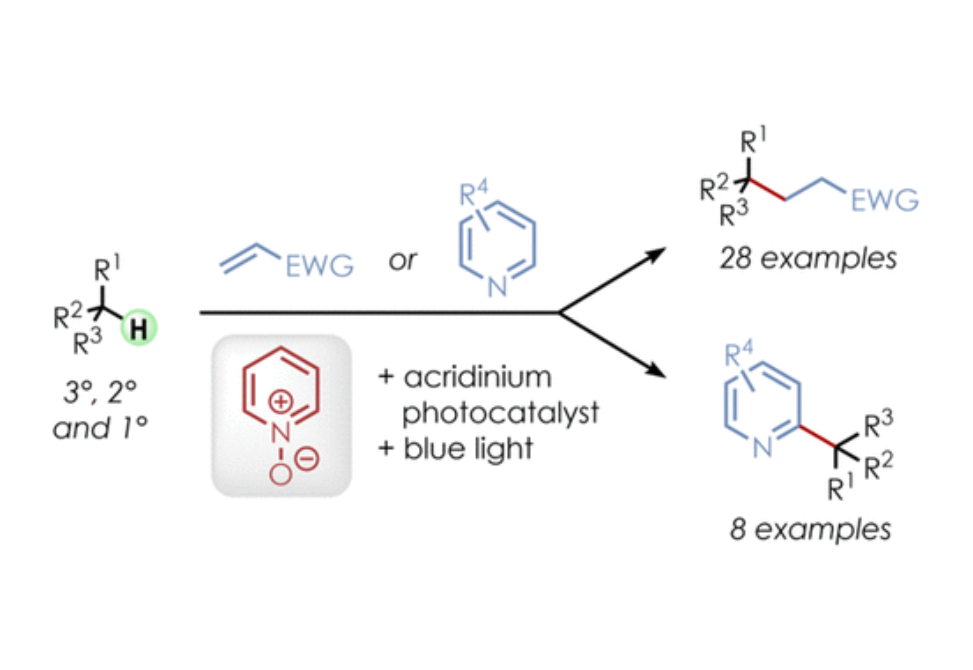
The alkylation and heteroarylation of unactivated tertiary, secondary, and primary C(sp3)–H bonds was achieved by employing an acridinium photoredox catalyst along with readily available pyridine N-oxides as hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) precursors under visible light.
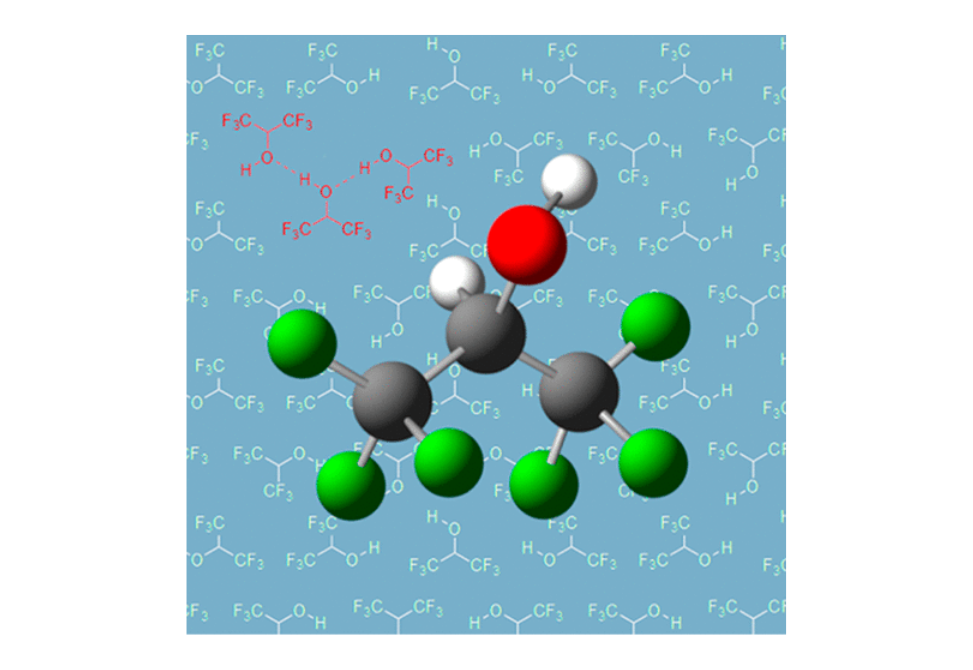
In this review, following a brief history of HFIP in organic synthesis and an overview of its physical properties, literature examples of organic reactions using HFIP as a solvent or an additive are presented, emphasizing the effect of solvent of each reaction.
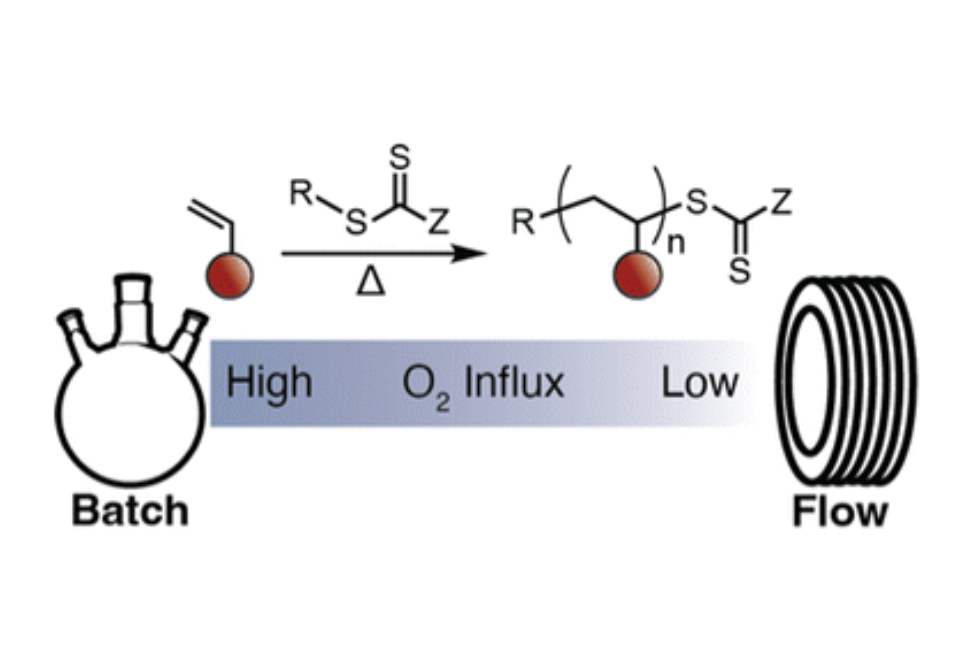
Herein we report a broadly applicable approach to “polymerize through” oxygen using the synergistic combination of two radical initiators having different rates of homolysis.
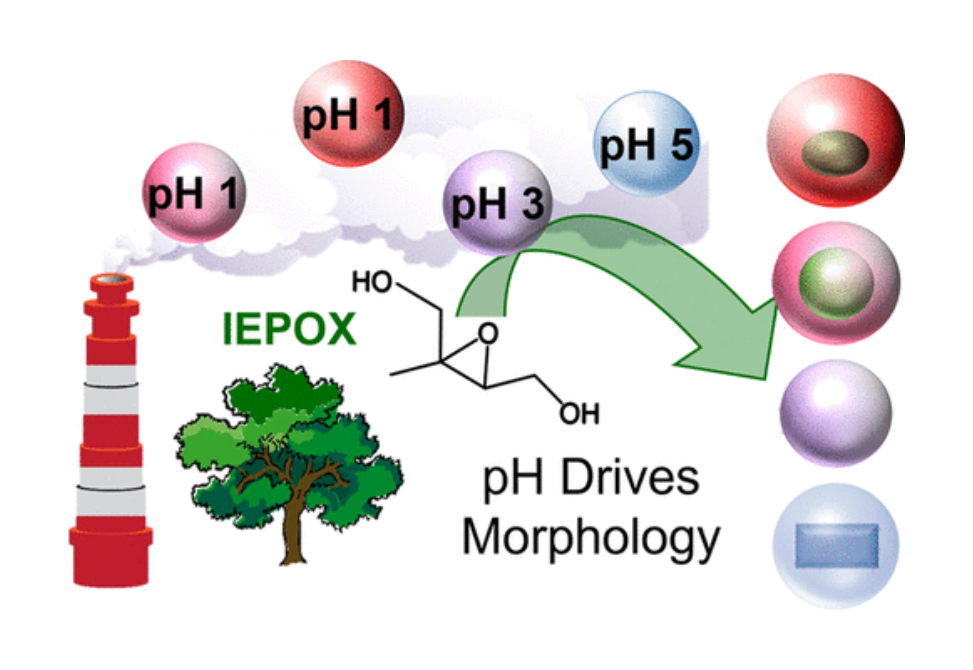
Herein, we show distinct differences in the morphology, phase state, and chemical composition of individual organic–inorganic mixed particles after IEPOX uptake to ammonium sulfate particles with different initial atmospherically relevant acidities (pH = 1, 3, and 5).