Department News
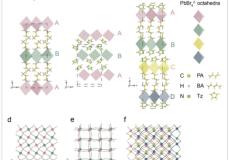
A Department of Chemistry study is shedding light on how a special class of materials called perovskites could help improve future optical technologies, from advanced sensors to telecommunications devices.

At a conference celebrated for scientific breakthroughs, graduate students are turning the spotlight onto the hidden risks faced by scientists.

Kevin Weeks, Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at UNC-Chapel Hill, has been named a Senior Member of the National Academy of Inventors.
Gary Pielak has received a Distinguished Scholar Fellowship from the Fulbright U.S. Scholar Program that will fund a four-month research residency in Israel.
Research

Herein, an approach for discriminating between tardigrade morphological states is developed and utilized to compare sucrose- and CaCl2-induced tuns, using the model species Hypsibius exemplaris.

Herein, we disclose a backbone rearrangement approach to tune the short-chain branching of polymers.
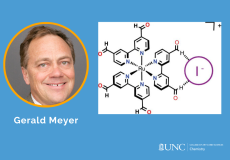
A new homoleptic Ru polypyridyl complex bearing two aldehyde groups on each bipyridine ligand, [Ru(dab)3](PF6)2, where dab is 4,4′-dicarbaldehyde-2,2′-bipyridine, was synthesized, characterized, and utilized for iodide photo-oxidation studies.
Connect