Research Archive
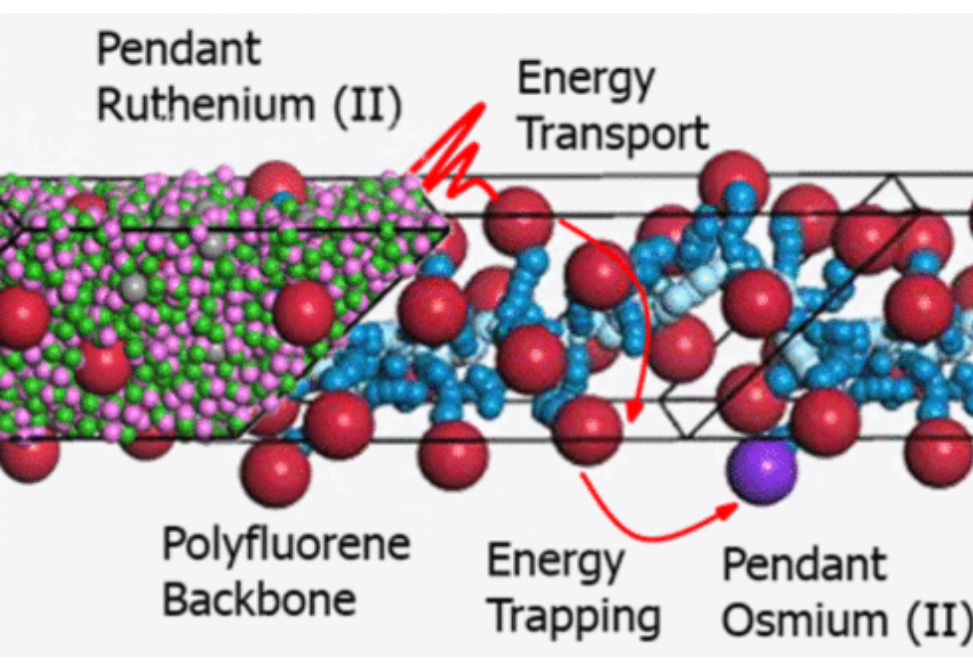
We investigate the mechanism of energy transfer between ruthenium(II) (Ru) and osmium(II) (Os) polypyridyl complexes affixed to a polyfluorene backbone (PF-RuOs) using a combination of time-resolved emission spectroscopy and coarse-grained molecular dynamics (CG MD).
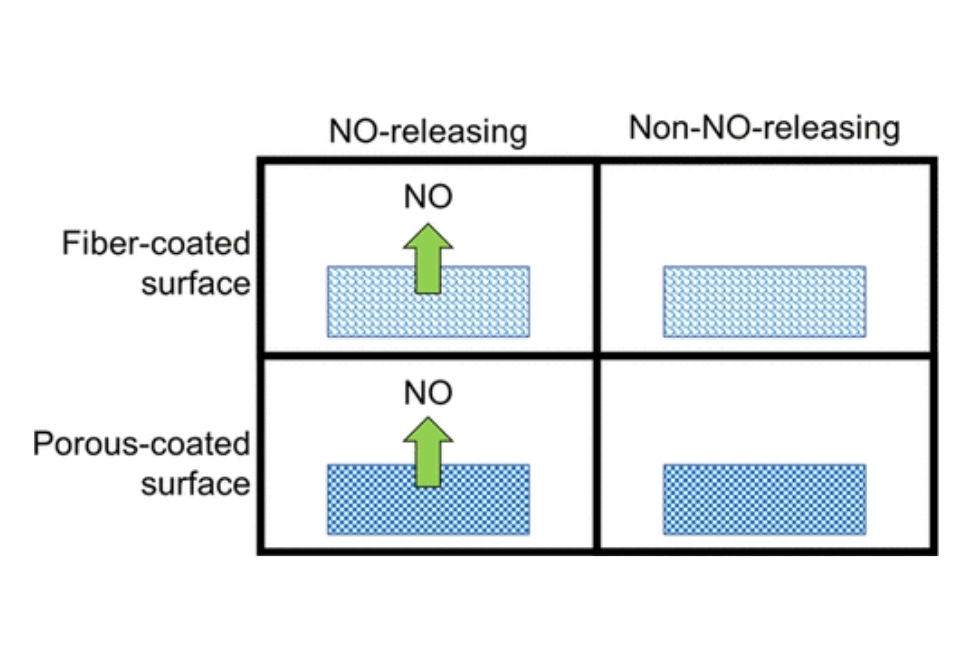
The tissue response to polyurethane (PU)-coated implants employing active and/or passive FBR mitigation techniques was evaluated over a 28 day study in a diabetic swine model.
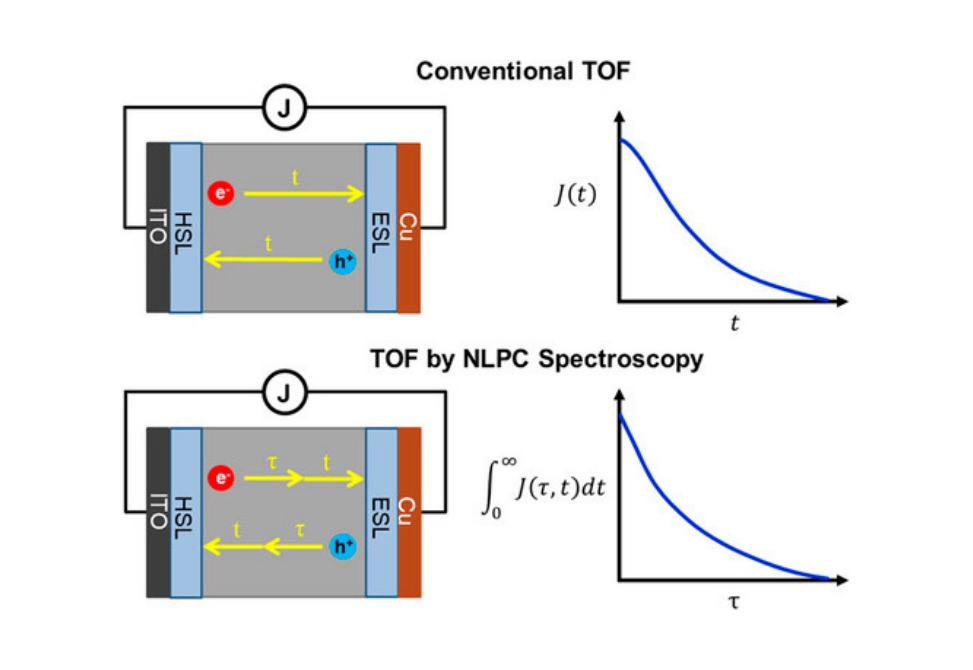
We present a multidimensional time-of-flight technique in which carrier transport is tracked with a second intervening laser pulse.
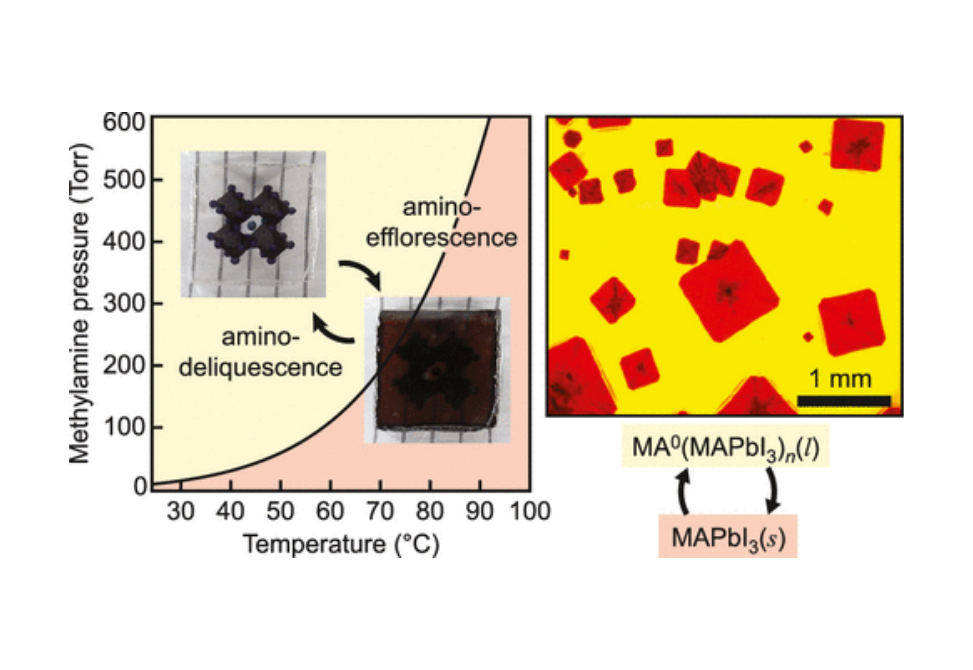
Here, using in situ spectroscopy and microscopy, we examine the thermodynamics and kinetics of the liquefaction and recrystallization of methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3) films with MA0 and find that the phenomena are best described as amino-deliquescence and amino-efflorescence, respectively.

Here, we demonstrate rate enhancement of up to two orders of magnitude for enzymes trapped in submicrometer water nanodroplets suspended in 1,2-dichloroethane.

This review highlights recent advances in plant proteomics, with an emphasis on spatially and temporally resolved analysis of post-translational modifications and protein interactions.
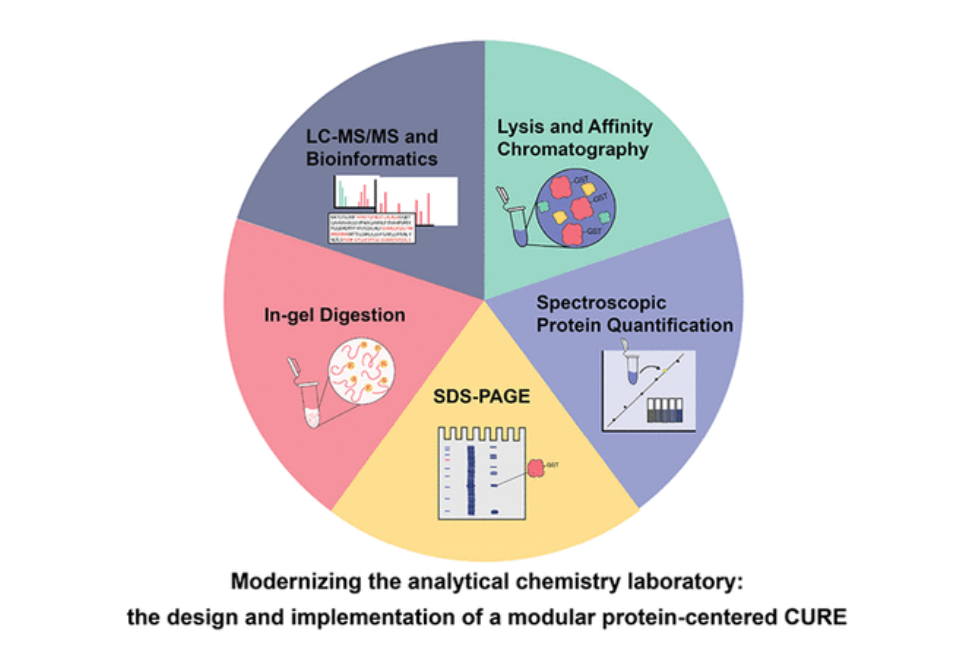
Through the implementation of the five modules, students apply the fundaments of acid–base chemistry, statistics, quantification strategies, spectrophotometry, separations, and mass spectrometry, thus covering the material required in most undergraduate introductory analytical courses.
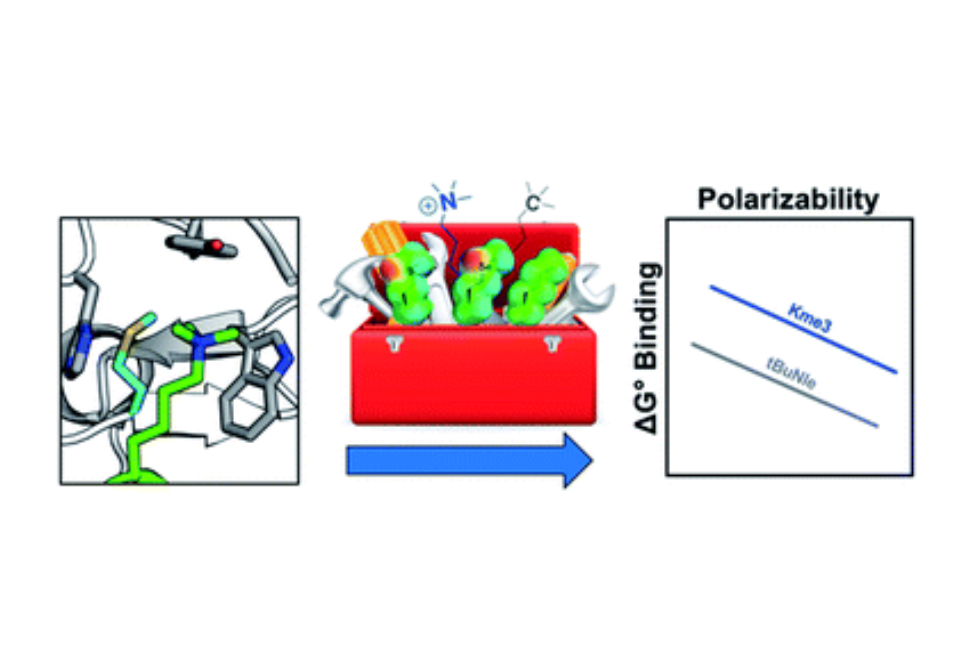
Our studies demonstrate that Met contributes to binding via dispersion forces, with about an equal contribution to binding Kme3 and tBuNle, indicating that electrostatic interactions do not play a role.
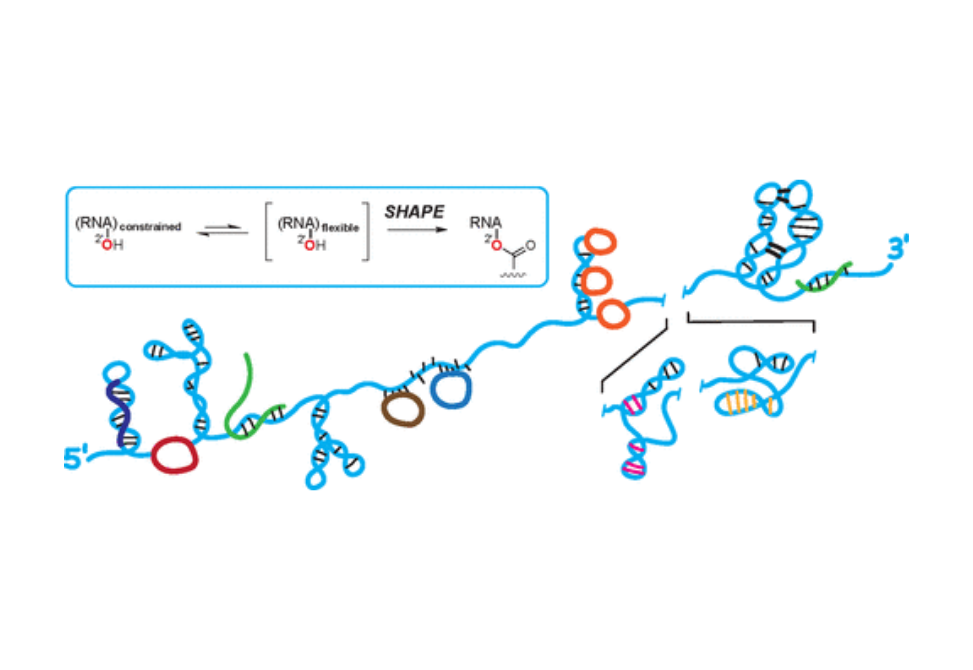
By applying comprehensive structure probing to diverse problems, we and others are showing that control of biological function mediated by RNA structure is ubiquitous across prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.
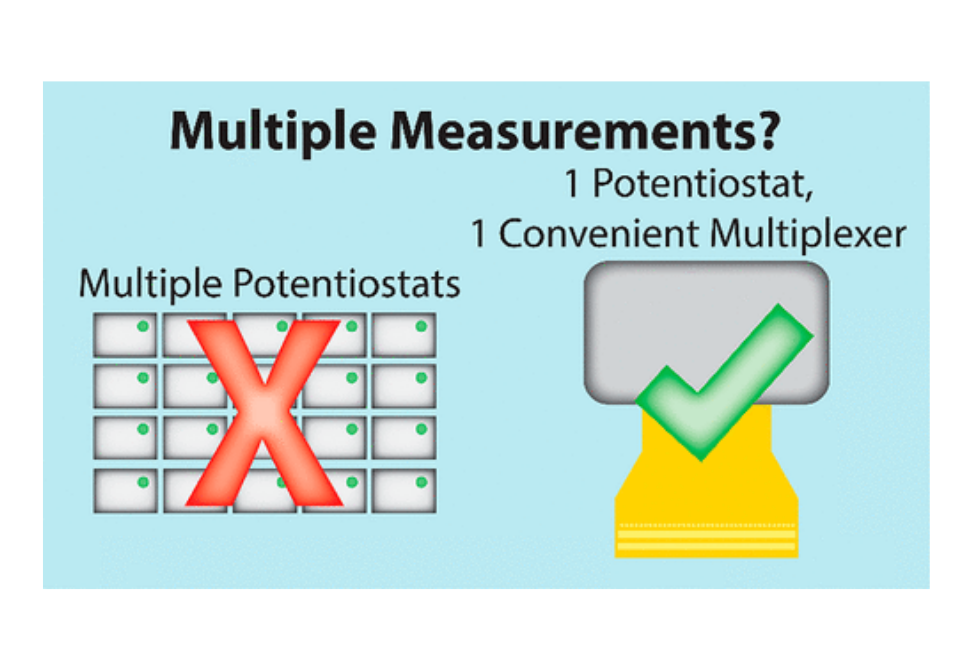
We present a versatile strategy for the development of flexible printed circuit (FPC) electrode arrays with accompanying multiplexing hardware to interface with single-channel potentiostats.
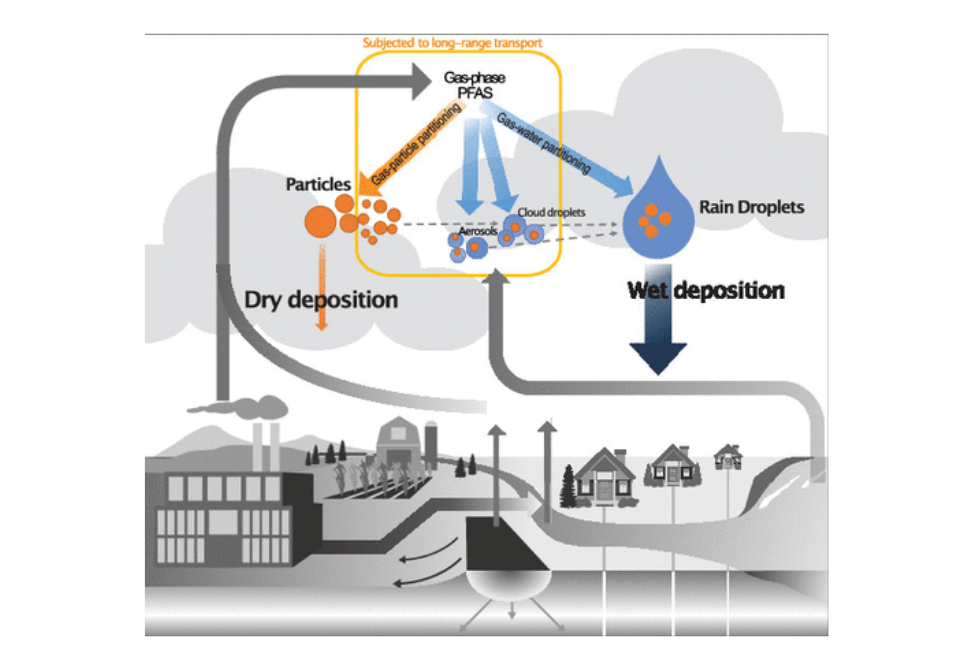
This study shows the first direct evidence of PFECAs in wet and dry deposition. The data suggest that the particle-bound and gas-phase PFAS that may have undergone long-range transport can be incorporated into raindrops and removed rapidly.