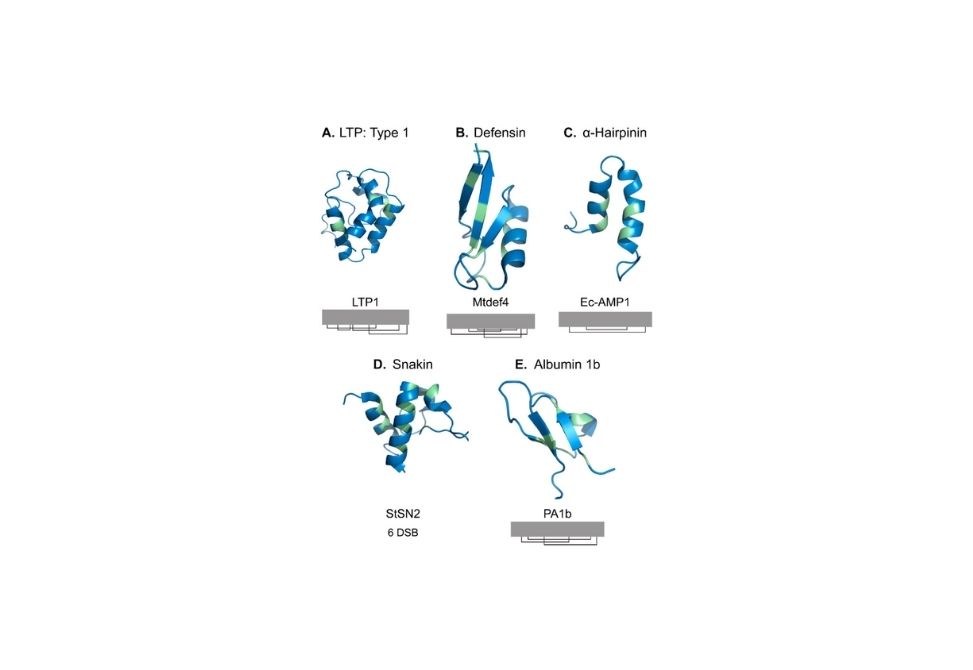
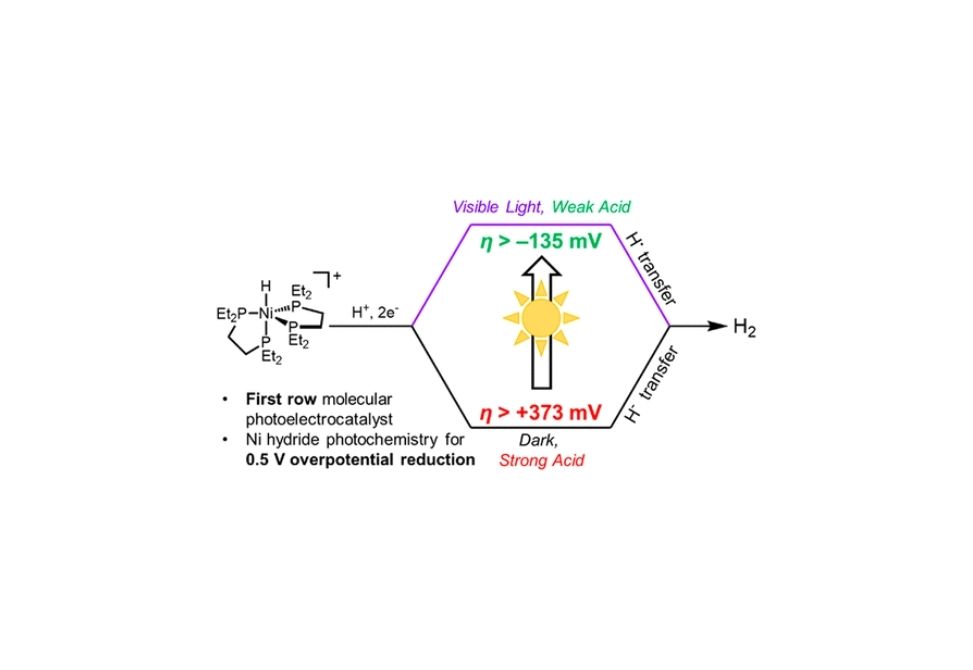
Research Archive
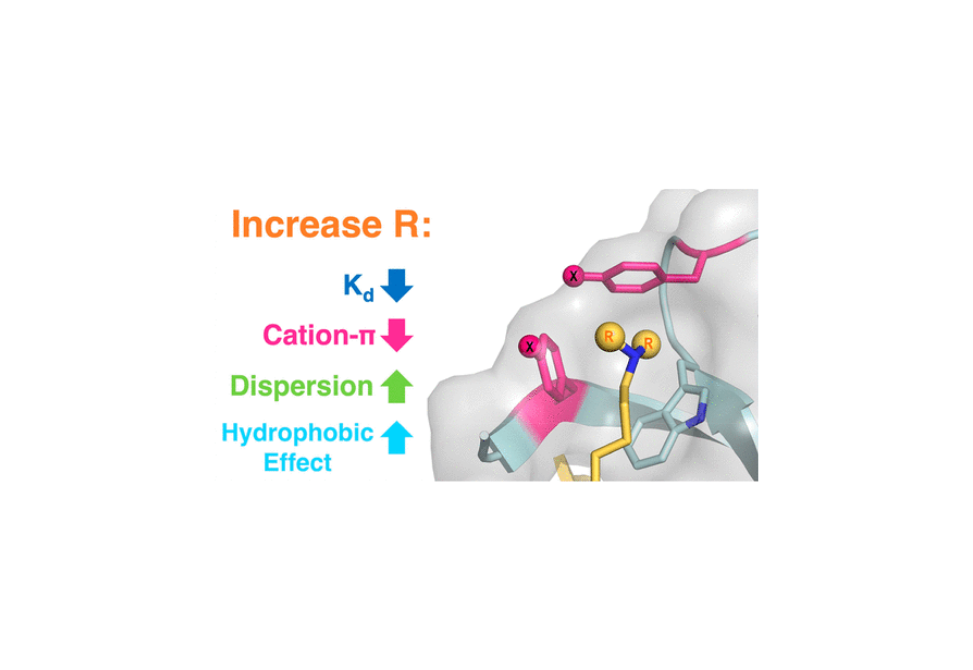
This study describes the development of a two-pronged approach combining genetic code expansion (GCE) and structure–activity relationships (SAR) through systematic variation of both the aromatic binding pocket in the protein and the alkyllysine residues in the peptide to probe inhibitor recognition in the CBX5 chromodomain.
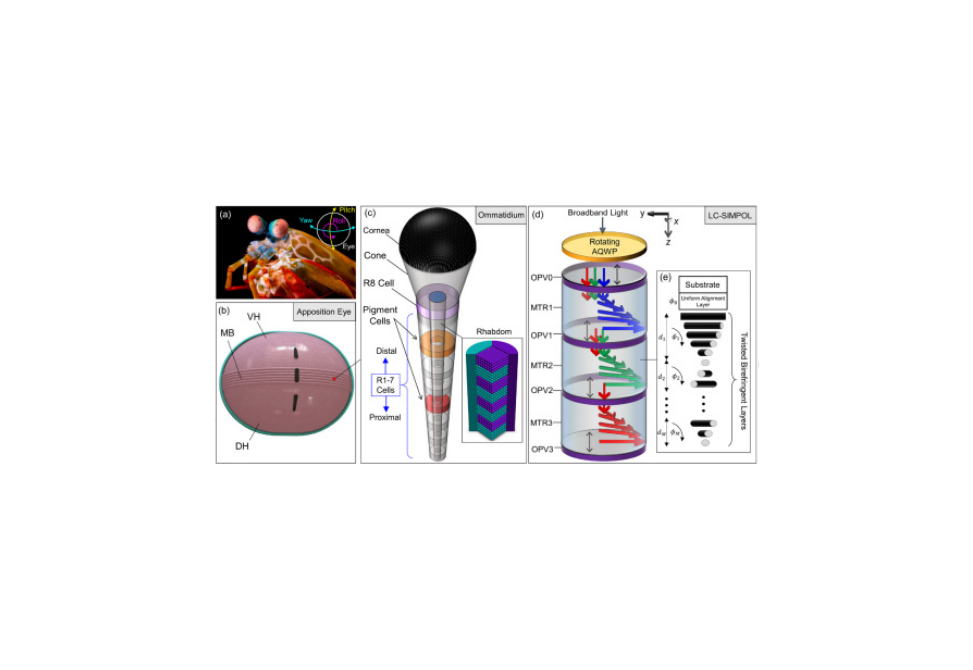
Here, we demonstrate a bio-inspired spectral and polarization sensor structure based on integrating semitransparent polarization-sensitive organic photovoltaics (P-OPVs) and liquid crystal polymer (LCP) retarders in a tandem configuration.
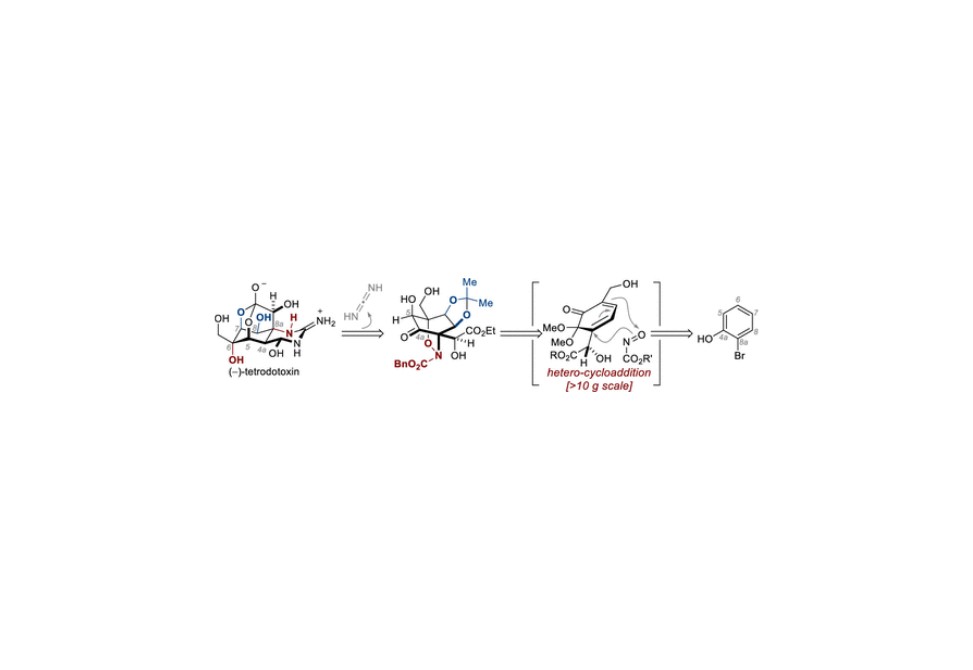
Progress toward a stereoselective synthesis of tetrodotoxin (TTX) is presented.
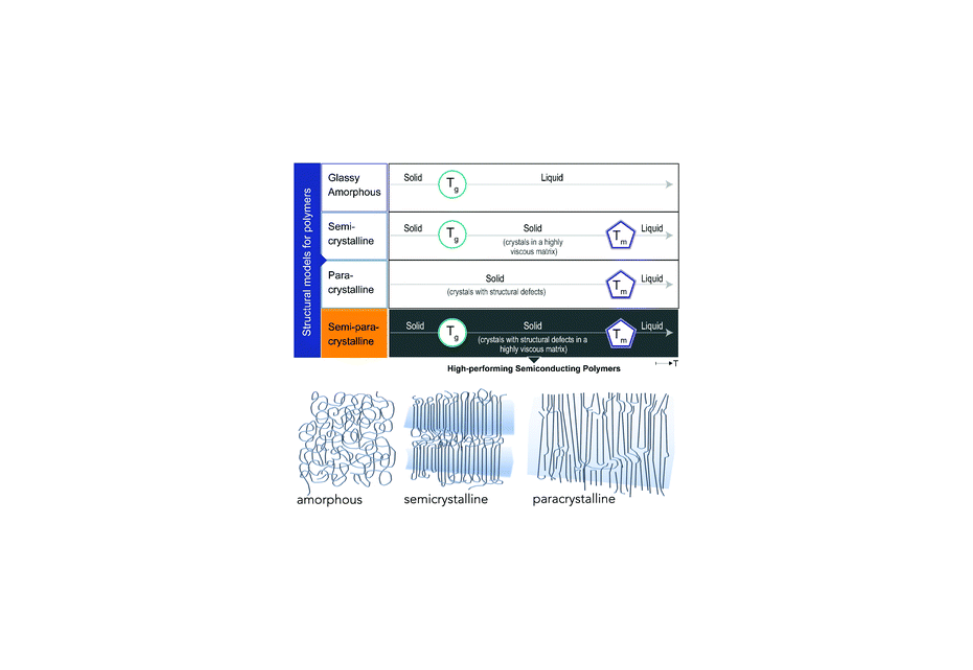
Prior characterization of some of the best-performing materials for transistor and photovoltaic applications, which are based on polymers with rigid backbones, often resulted in conundrums in which X-ray scattering and microscopy yielded seemingly contradicting results. Here we solve the paradox by introducing a new structural model, i.e., semi-paracrystalline organization.
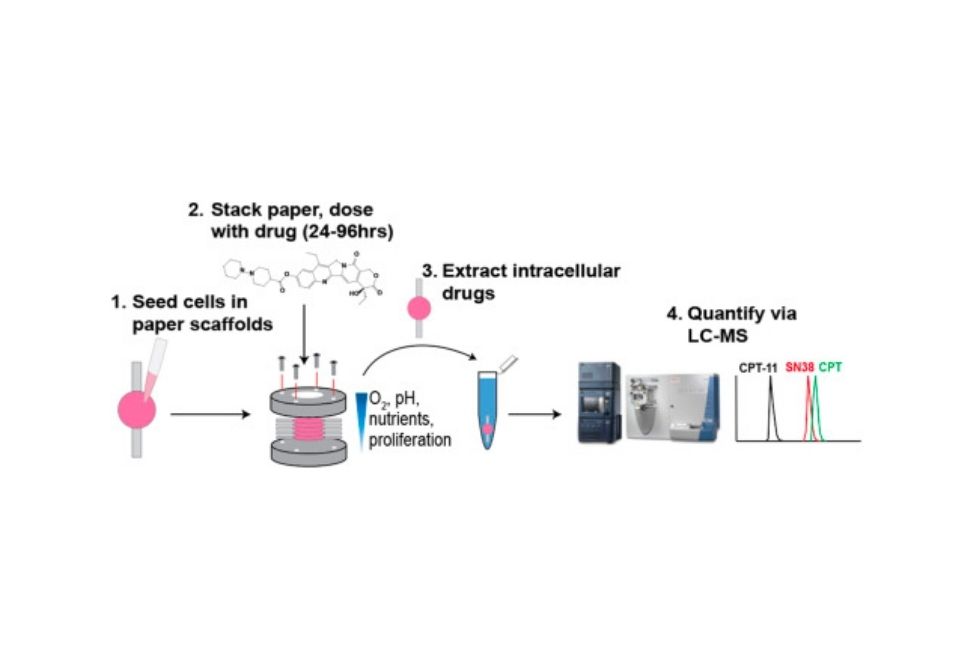
Here we describe a workflow in which cell viability, drug penetration, and drug metabolism are quantified in a spatially resolved manner.
Here we describe a workflow in which cell viability, drug penetration, and drug metabolism are quantified in a spatially resolved manner.
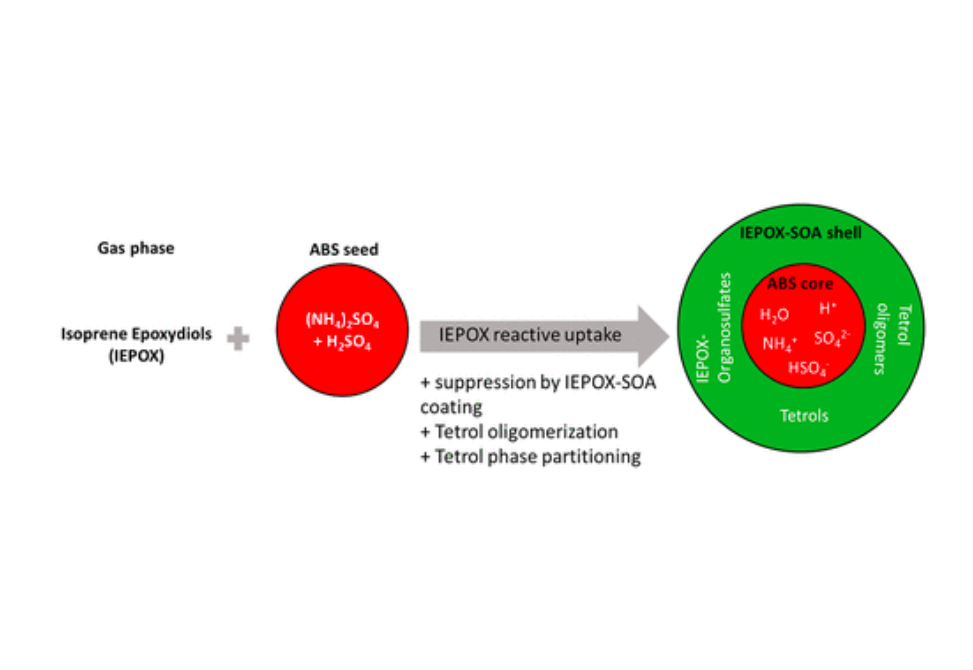
Here, we implement our latest understanding of IEPOX-SOA formation within a box model to simulate the measured reactive uptake of IEPOX on polydisperse ammonium bisulfate seed aerosols within an environmental Teflon chamber.
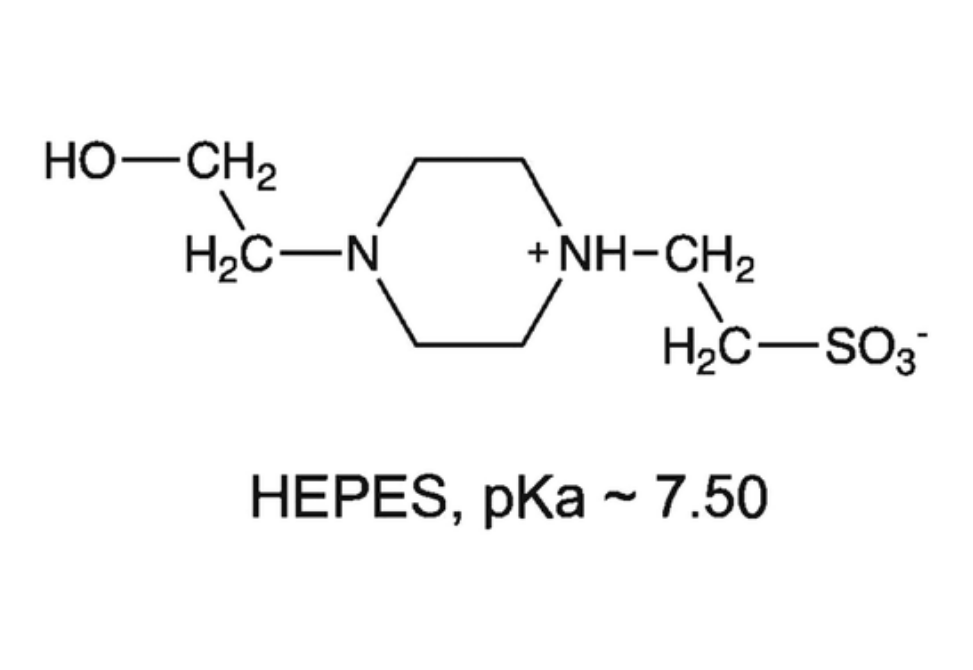
Here, I discuss some of the background regarding the genesis of “Good’s buffers”, make a few (disparaging) observations about the non-Good’s buffer, Tris, and suggest that we synthesize new buffers by combining the ideas of Good et al. with results from the past 60 years of protein chemistry.