Research Archive
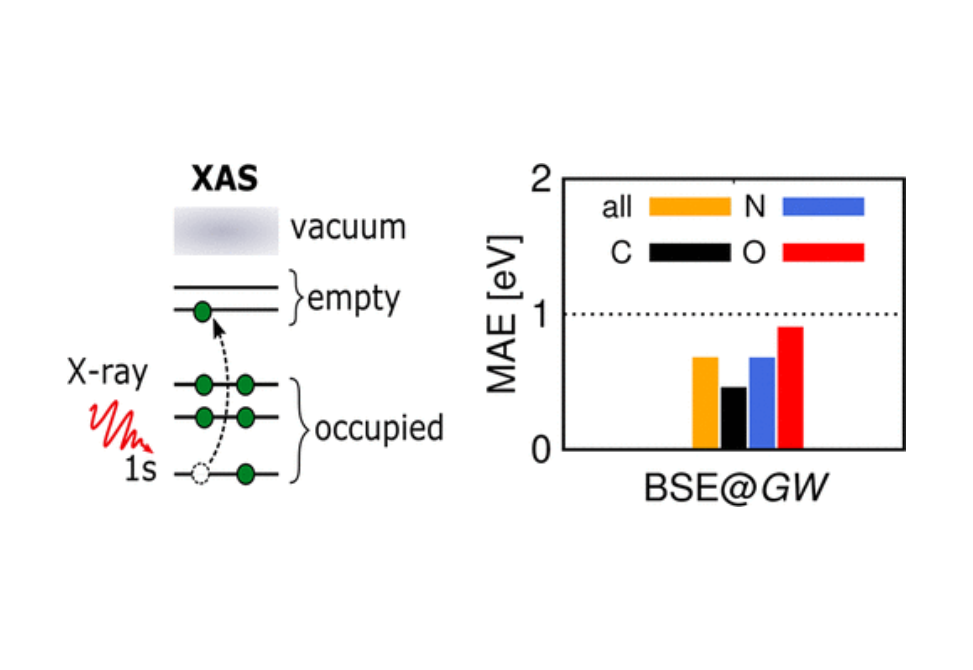
We present an accurate computational approach to calculate absolute K-edge core electron excitation energies as measured by X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
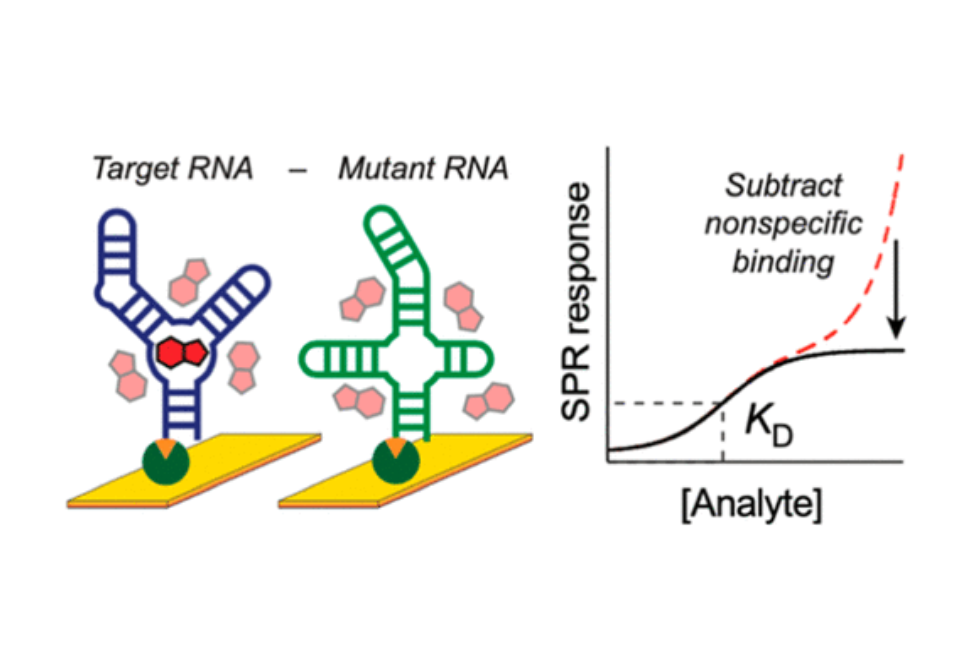
Here, we show that referencing to a channel containing a non-binding control RNA enables subtraction of nonspecific binding contributions, allowing measurements of accurate and specific binding affinities.
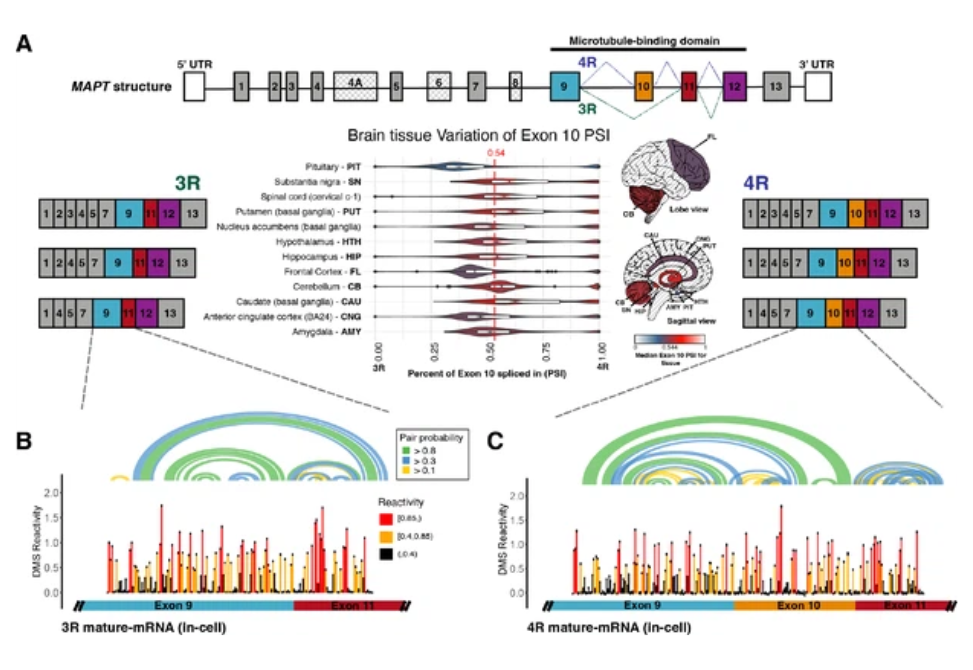
Here we use a novel chemical probing strategy to visualize endogenous precursor and mature MAPT mRNA structures in cells.
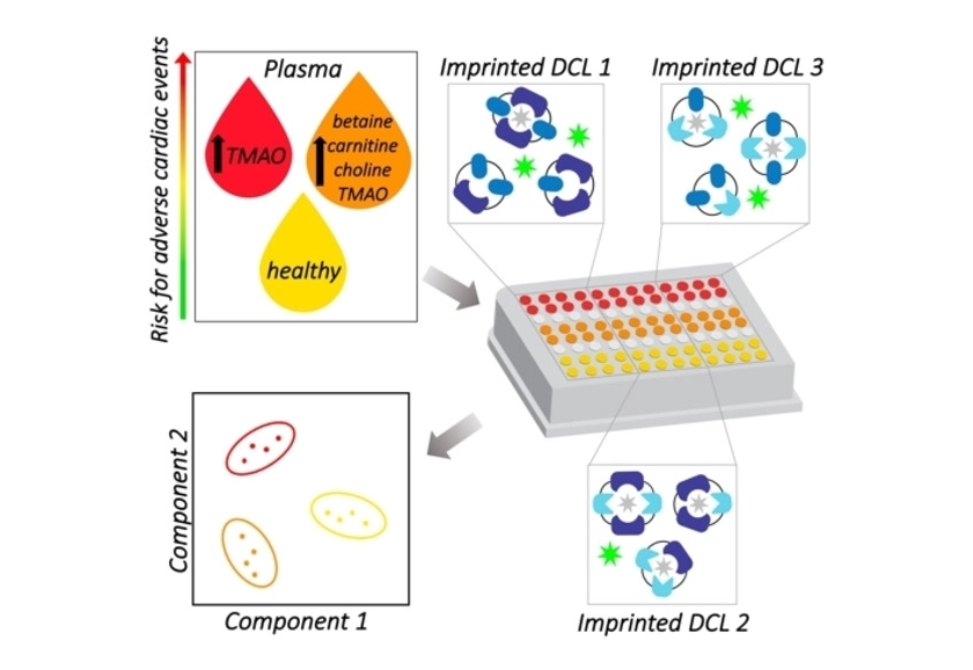
Thus, we have adapted our previously described "imprint-and-report" fluorescent sensing method using dynamic combinatorial libraries (DCLs) to create a sensor array for these four metabolites that functions at physiologically relevant concentrations.
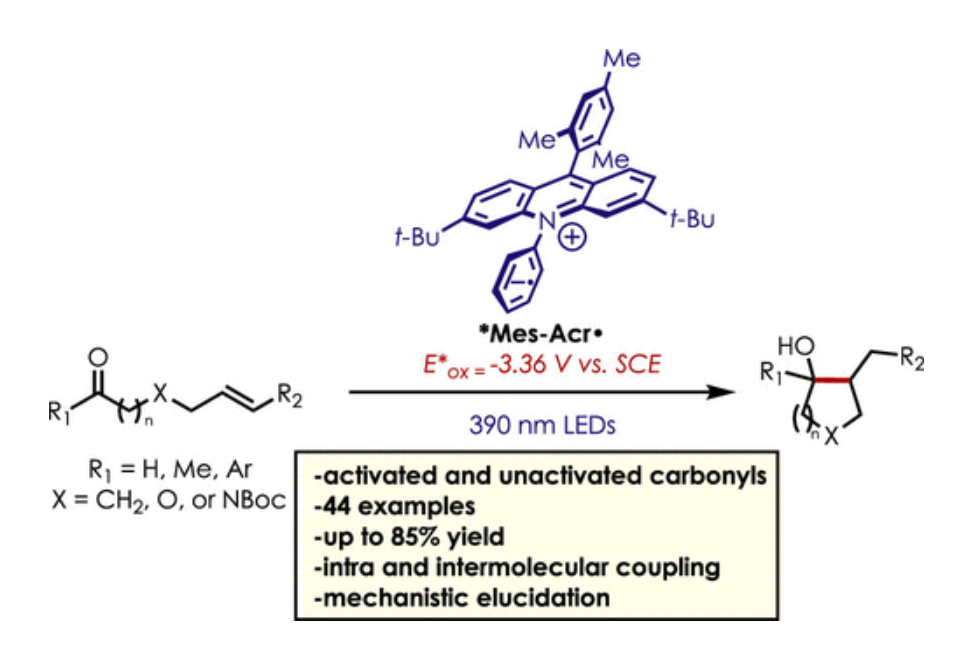
Herein, we describe a mild, metal-free ketone–olefin coupling reaction using an excited-state acridine radical super reductant as a photoredox catalyst.

I am pleased to dedicate this SYNLETT Cluster in honor of Professor Shunichi Fukuzumi's 70th birthday. Prof. Fukuzumi is currently a Distinguished Professor at Ewha Womans University, Seoul, South Korea and Professor Emeritus of Osaka University, Japan.
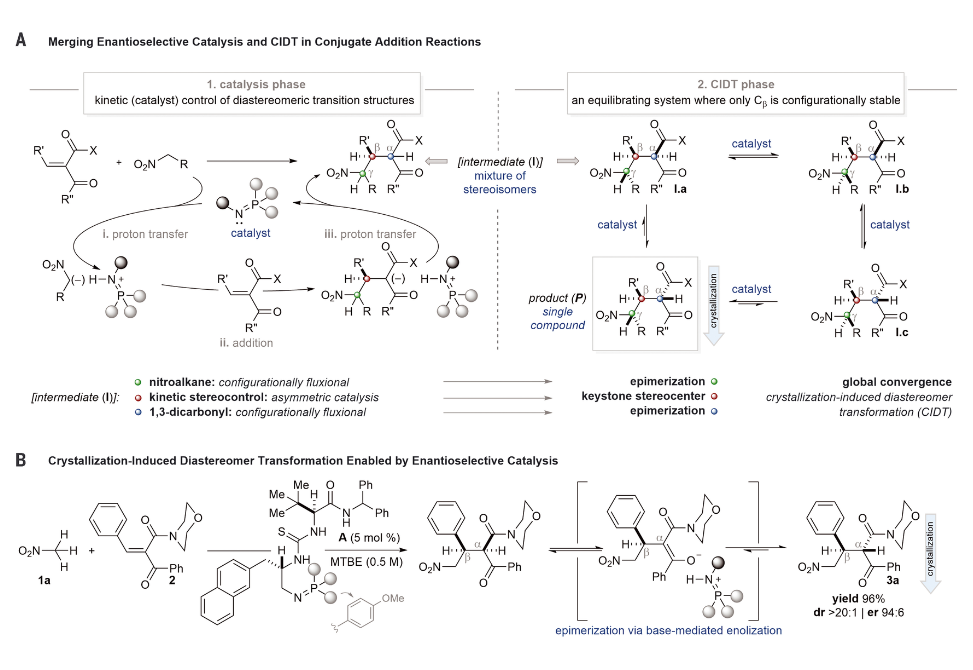
Herein, we report the discovery and development of a catalyst-mediated asymmetric Michael addition/crystallization–induced diastereomer transformation of broad scope.
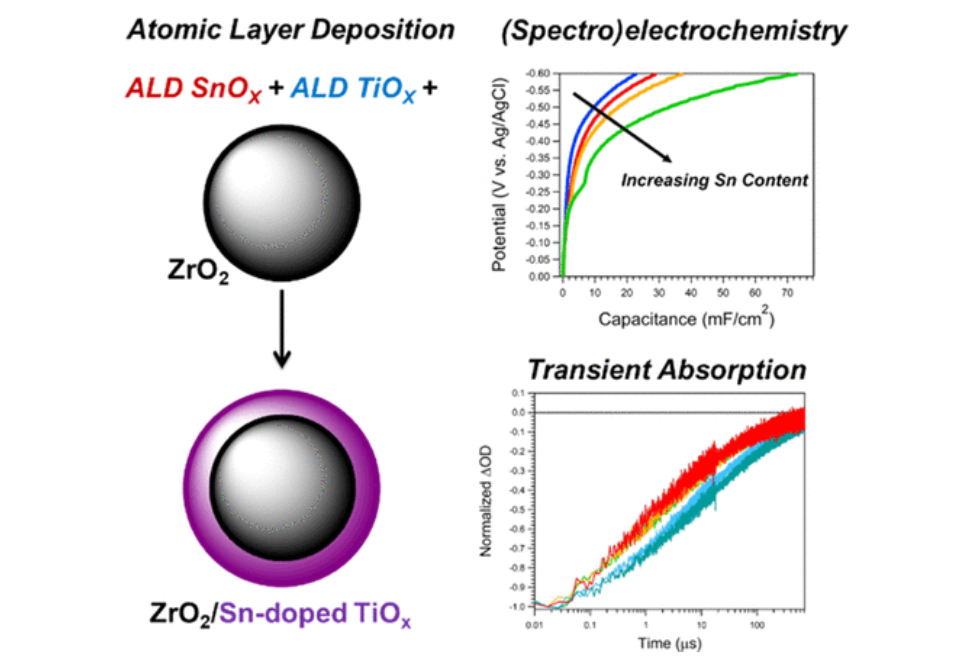
We demonstrate that the insulating ZrO2 substrate allows for the (spectro)electrochemical analysis of ultrathin ALD coatings to assess the electronic structure as a function of composition.
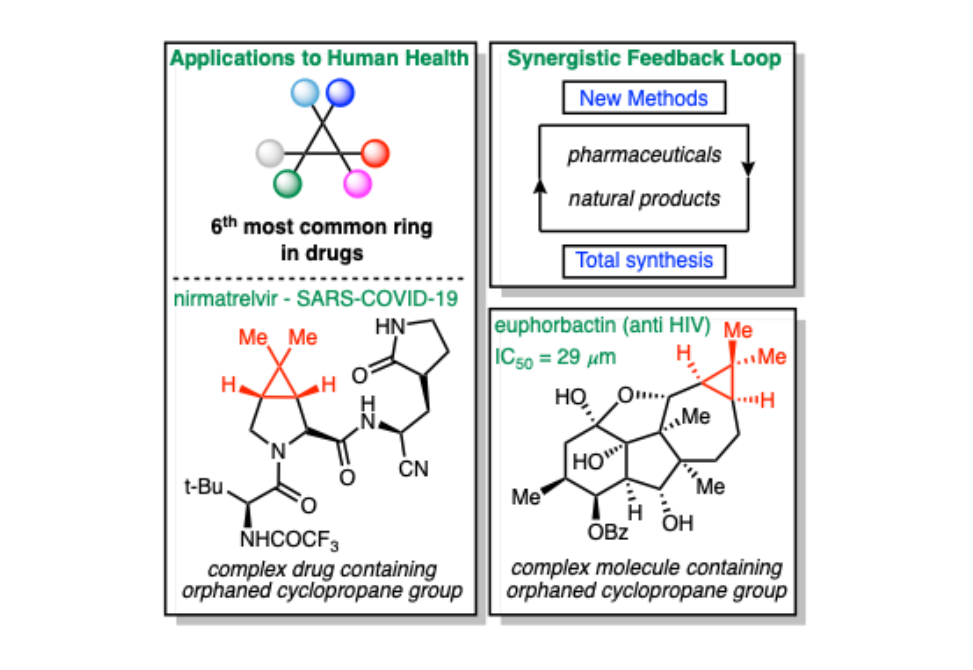
In an effort to rescue these “orphaned” cyclopropanes, Wilkerson-Hill and co-workers devised a stepwise addition/1,3-elimination process involving sterically encumbered dialkylmethine-substituted tert-butyl sulfones and styrenes.
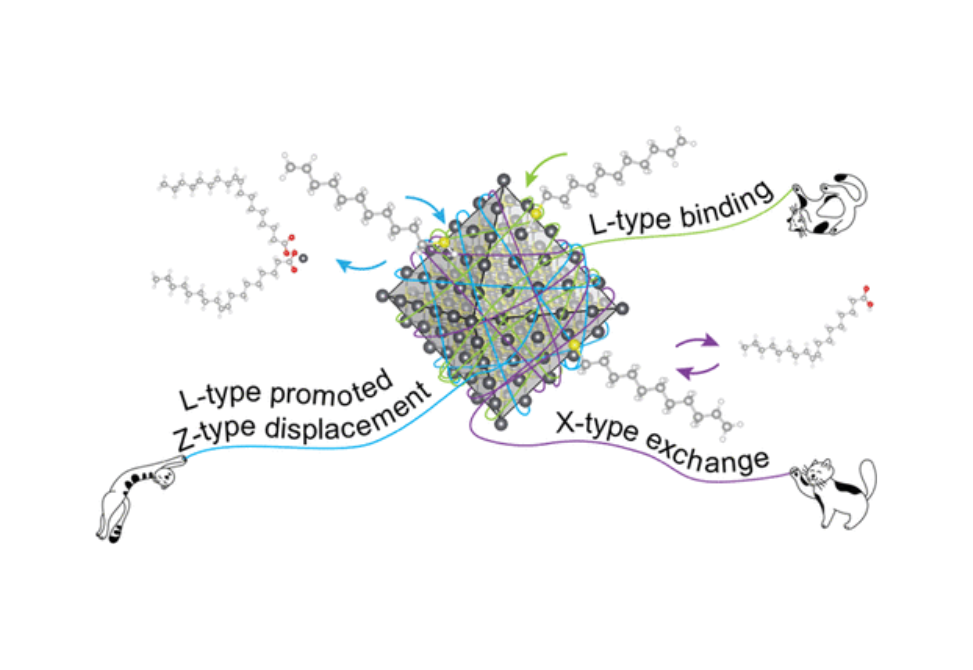
Here, we report three separate ligand-based reaction mechanisms between oleate-capped PbS NCs and the exchange thiol ligand, undec-10-ene-1-thiol (UDT), and unveil how these three pathways are intertwined.
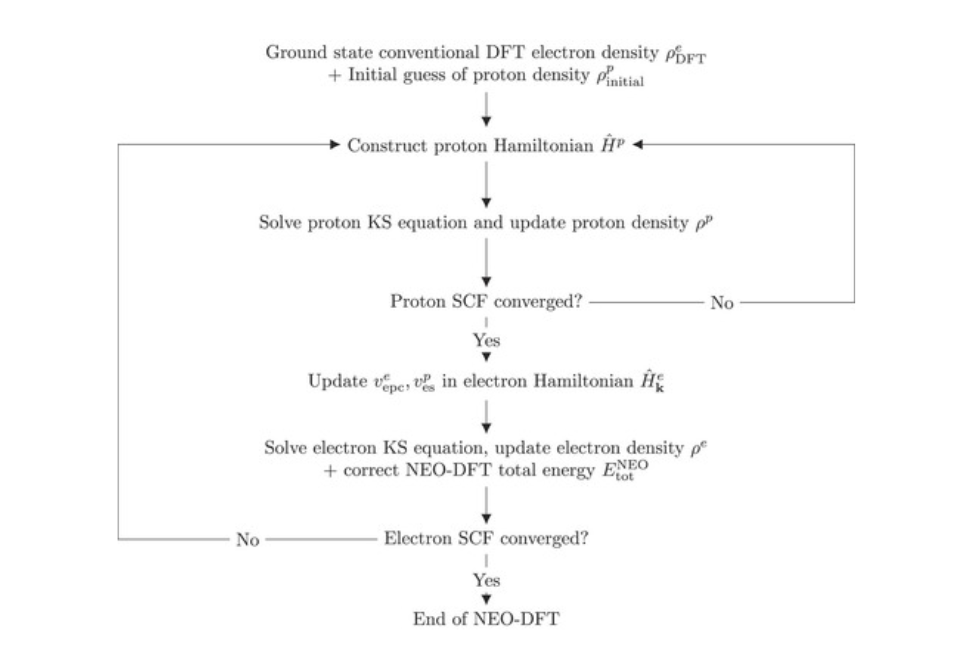
In this work, we present a strategy to implement the NEO method for periodic electronic structure calculations, particularly focused on multicomponent density functional theory (DFT).
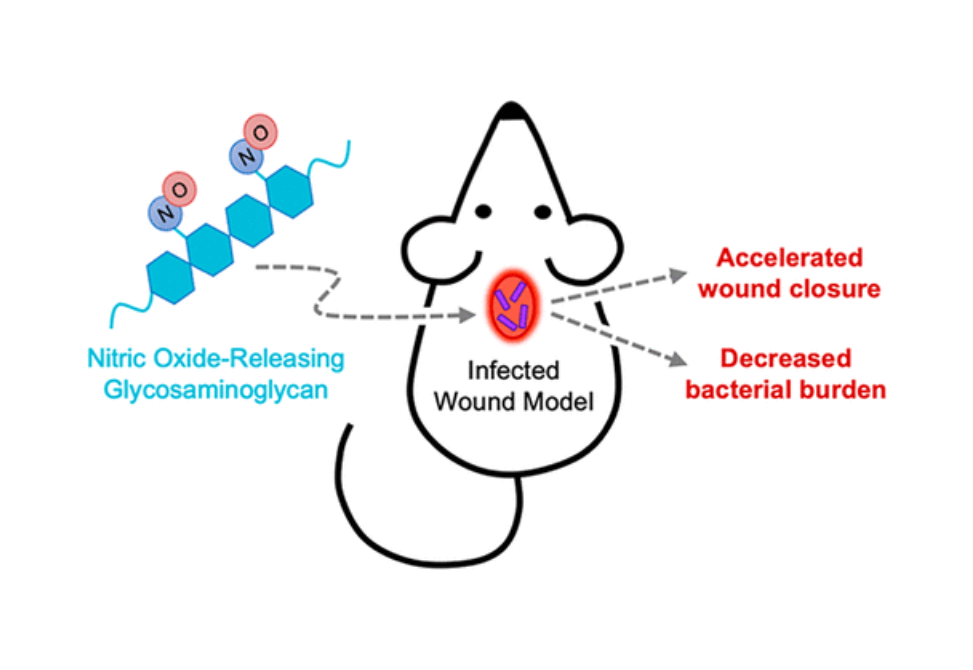
Two glycosaminoglycan (GAG) biopolymers, hyaluronic acid (HA) and chondroitin sulfate (CS), were chemically modified via carbodiimide chemistry to facilitate the loading and release of nitric oxide (NO) to develop a multi-action wound healing agent.