Ketone-Olefin Coupling of Aliphatic and Aromatic Carbonyls Catalyzed by Excited-State Acridine Radicals
Abstract
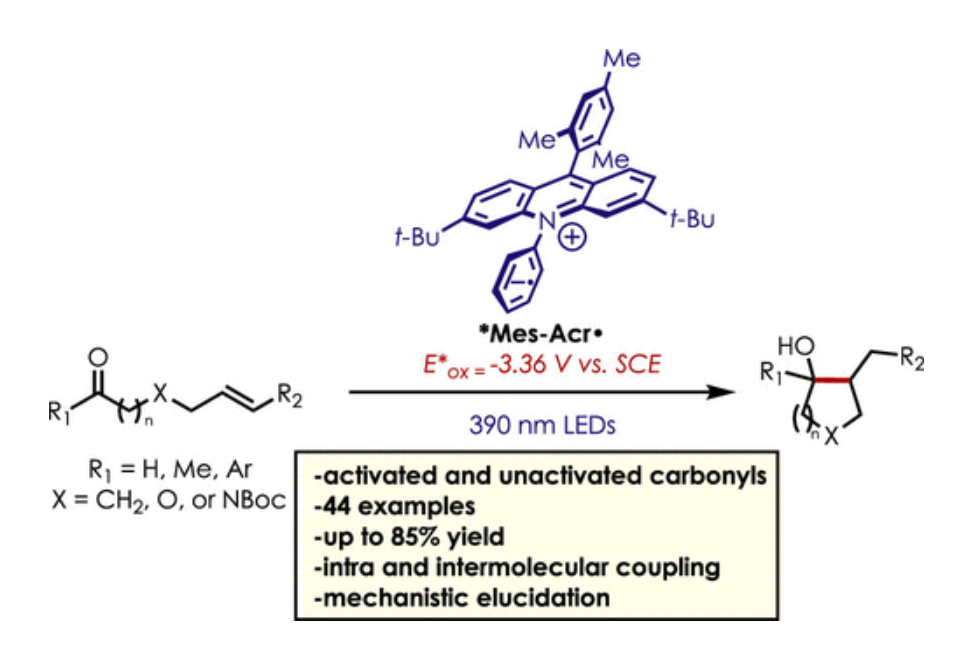
Ketone–olefin coupling reactions are common methods for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. This reaction class typically requires stoichiometric or super stoichiometric quantities of metal reductants, and catalytic variations are limited in application. Photoredox catalysis has offered an alternative method toward ketone–olefin coupling reactions, although most methods are limited in scope to easily reducible aromatic carbonyl compounds. Herein, we describe a mild, metal-free ketone–olefin coupling reaction using an excited-state acridine radical super reductant as a photoredox catalyst. We demonstrate both intramolecular and intermolecular ketone–olefin couplings of aliphatic and aromatic ketones and aldehydes. Mechanistic evidence is also presented supporting an “olefin first” ketone–olefin coupling mechanism.
Citation
Ketone–Olefin Coupling of Aliphatic and Aromatic Carbonyls Catalyzed by Excited-State Acridine Radicals
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c04822