Research Archive
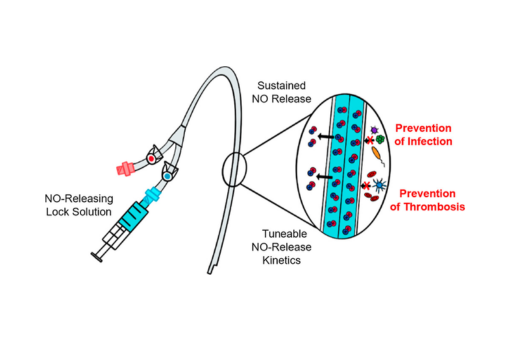
In an attempt to address the significant morbidity, mortality, and economic cost associated with tunneled dialysis catheter (TDC) dysfunction, we report the development of nitric oxide (NO)-releasing dialysis catheter lock solutions.
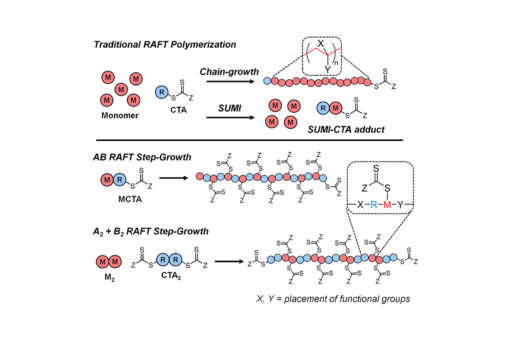
This review covers a brief history of the RAFT-SUMI process and its transformation into RAFT step-growth polymerization, followed by a comprehensive discussion of various RAFT step-growth systems.
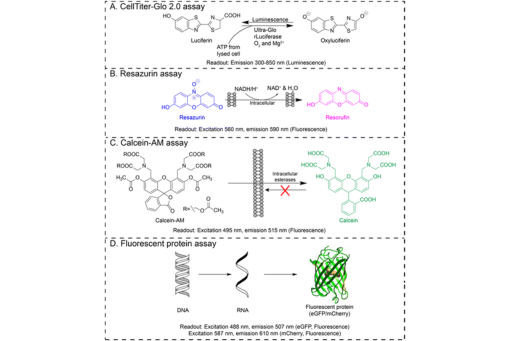
Here we determine the analytical figures of merit of five indirect viability assays in the paper-based cell culture platform we continue to develop in our laboratory: calcein-AM staining, the CellTiter-Glo assay, imaging fluorescent protein expression, propidium iodide staining, and the resazurin assay.

This perspective reviews recent studies of non-covalent interactions involving the π systems of organic cations in low-dimensional OIHPs.
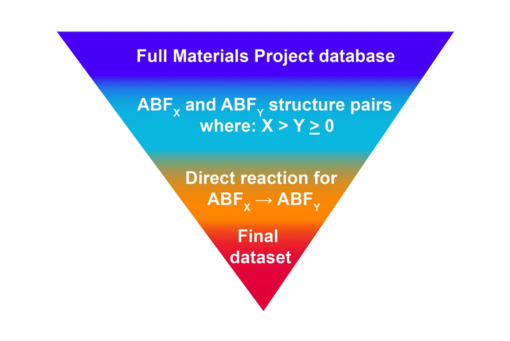
Here, we evaluate ternary fluorides from the Materials Project crystal structure database to identify promising cathode materials for FIBs.
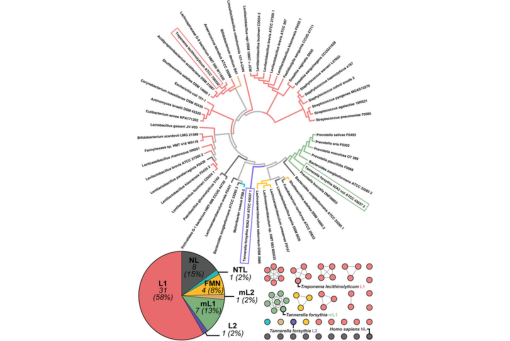
Here, we define the 53 unique GUSs in the human oral microbiome and examine diverse GUS orthologs from periodontitis-associated pathogens.
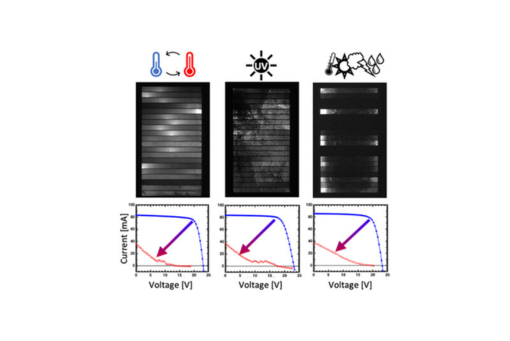
Herein, electroluminescence (EL) and thermal imaging are used to examine p–i–n metal halide perovskite (MHP) photovoltaic (PV) mini-modules (MA0.6FA0.4PbI3, 20 cells, 78 cm2) before and after indoor-accelerated stress testing or outdoor deployment.
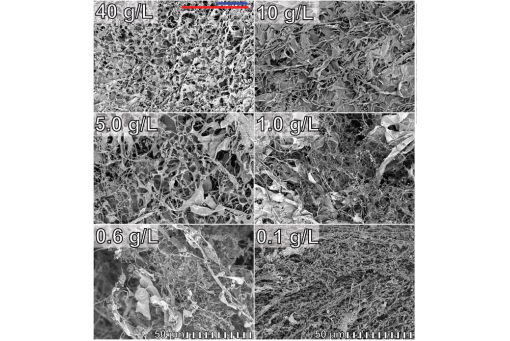
Here, we show that dried CAHS D gels (i.e., aerogels) retain the structural units of their hydrogels, but the details depend on prelyophilization CAHS concentrations.
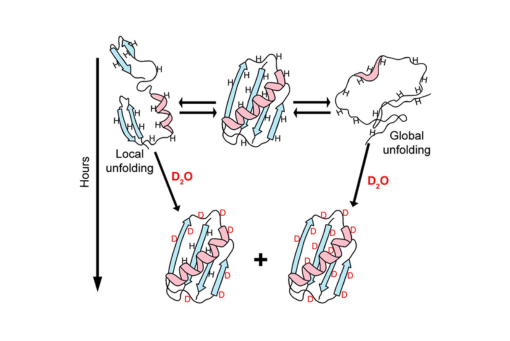
We review the use of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to assess the exchange of amide protons for deuterons (HDX) in efforts to understand how high concentration of cosolutes, especially macromolecules, affect the equilibrium thermodynamics of protein stability.
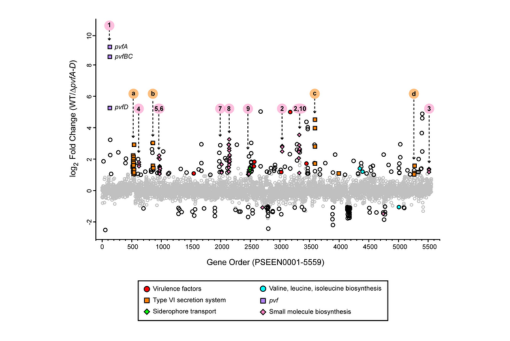
Here, we identified genes that are likely regulated by Pvf using the model strain P. entomophila L48 which does not contain other known quorum sensing systems.
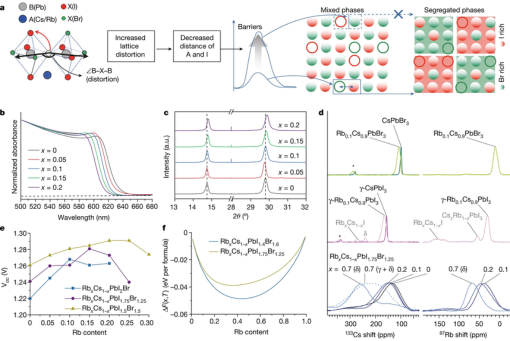
Here we report that lattice distortion in iodide/bromide mixed perovskites is correlated with the suppression of phase segregation, generating an increased ion-migration energy barrier arising from the decreased average interatomic distance between the A-site cation and iodide.