Research Archive
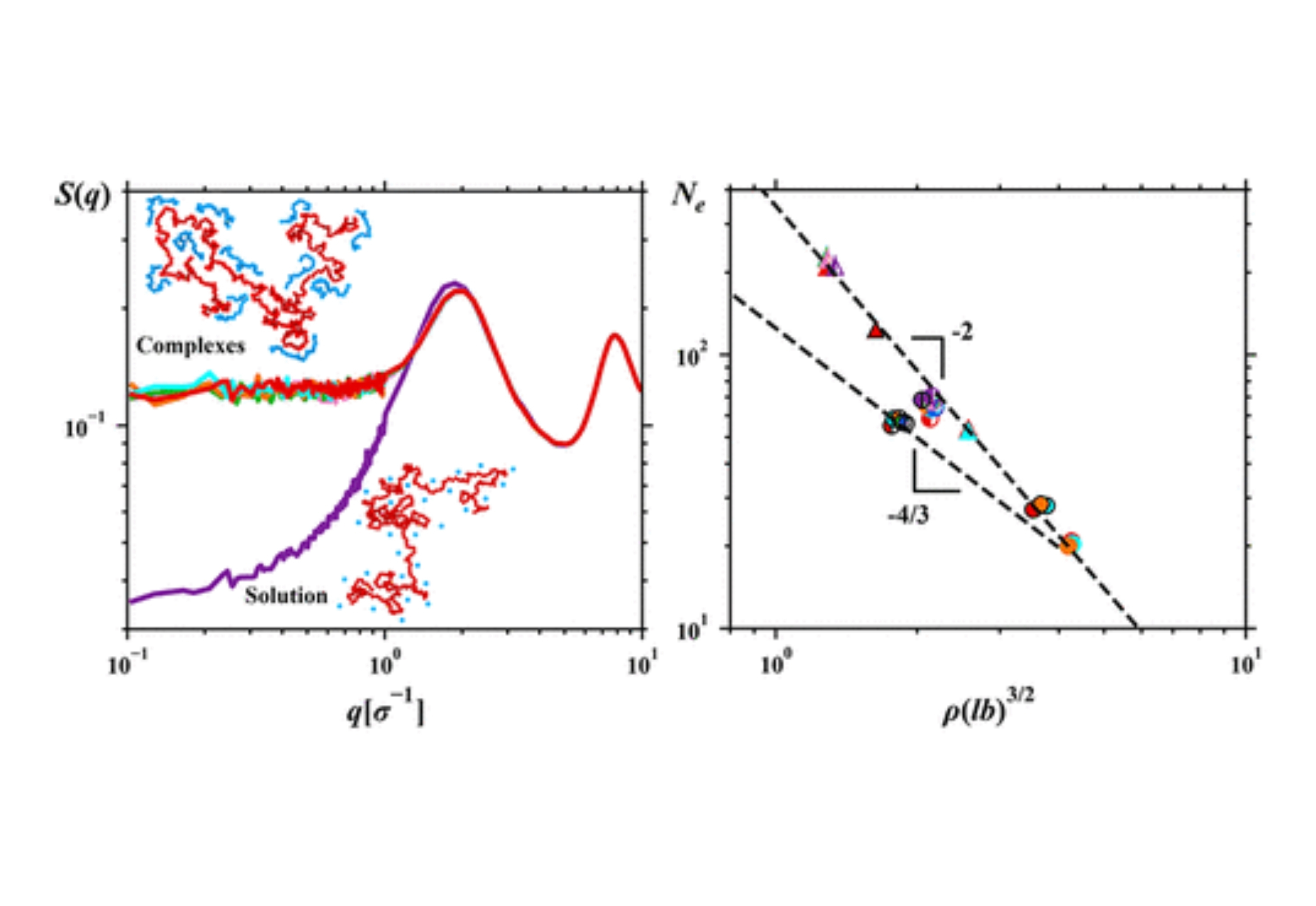
Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations, random phase approximation (RPA) approach, and scaling analysis are used to study static and dynamic properties of concentrated polyelectrolyte solutions of positively charged chains with the degree of polymerization N+ = 400 and their mixtures with negatively charged chains with degrees of polymerization N– varying between 10 and 400.
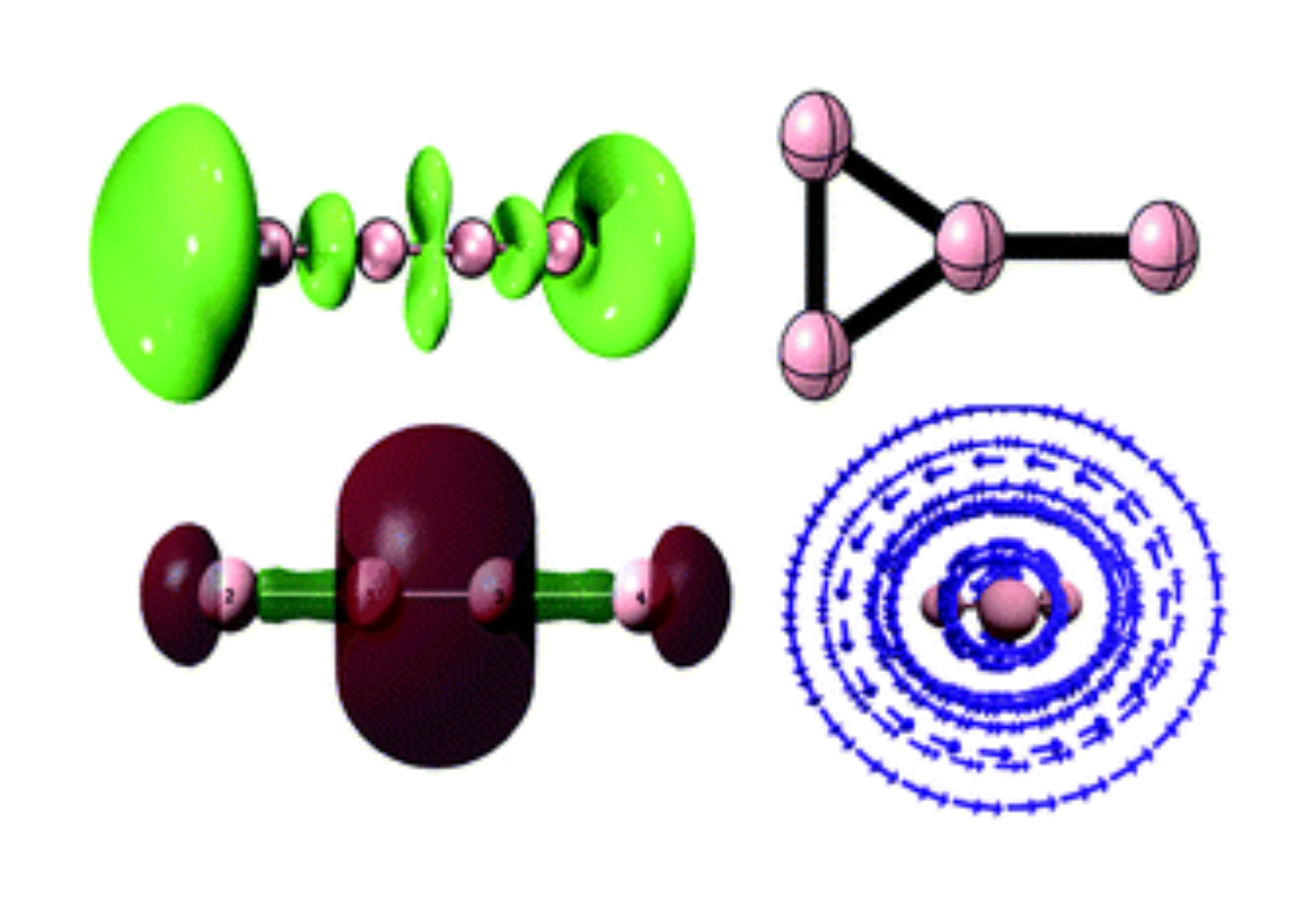
To unveil their unconventional properties, in this work, using neutral tetraboron clusters as illustrative examples, we study their exotic behaviors in bonding, aromaticity, and reactivity.
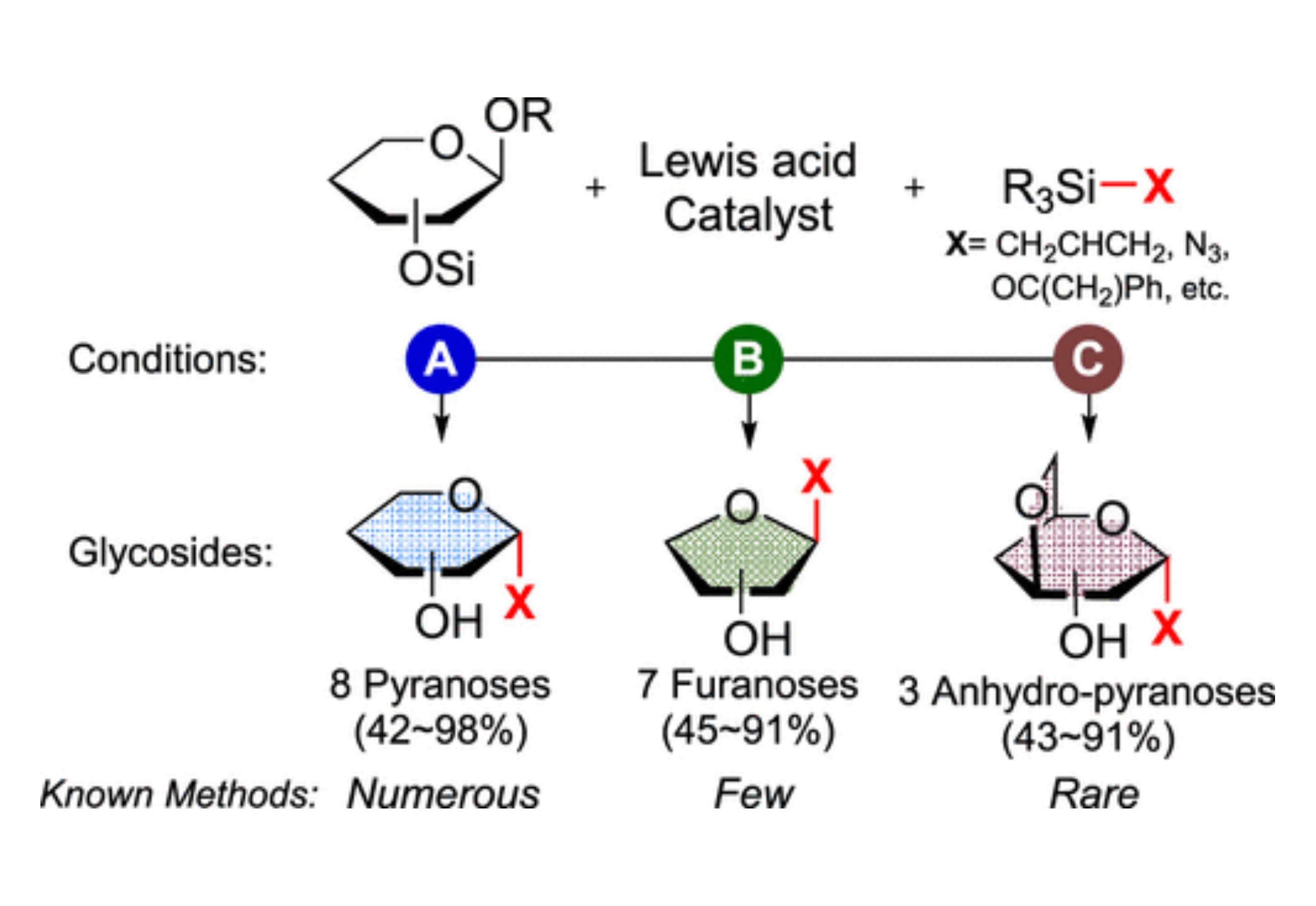
A variety of C-glycosides can be obtained from the fluoroarylborane (B(C6F5)3) or silylium (R3Si+) catalyzed functionalization of 1-MeO- and per-TMS-sugars with TMS-X reagents.
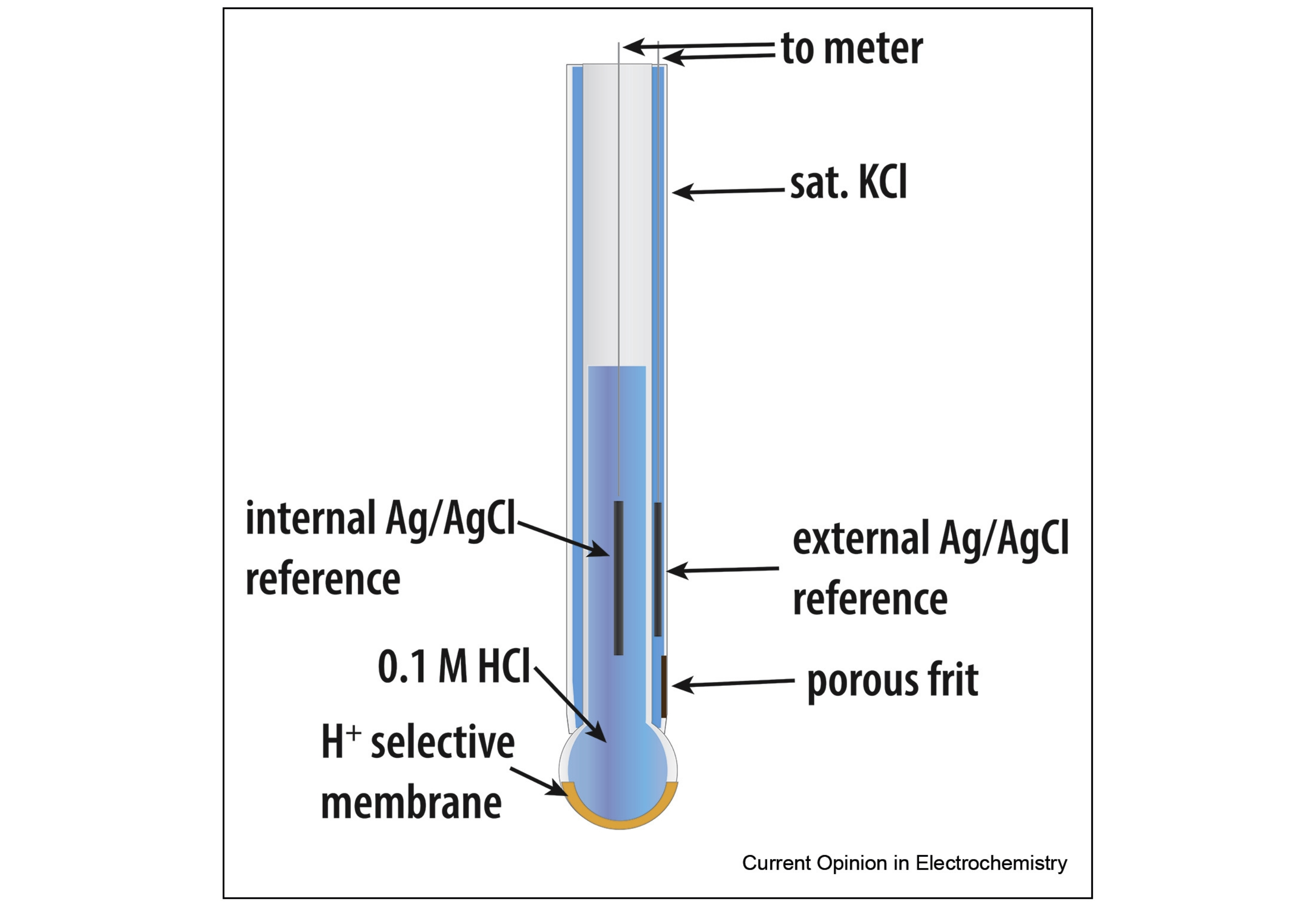
This mini-review on recent (2018–2020) advances in the field of potentiometric biosensors is intended to give a general overview of the main types of potentiometric biosensors for novices while still providing a brief but thorough summary of the novel advances and trends for experienced practitioners.
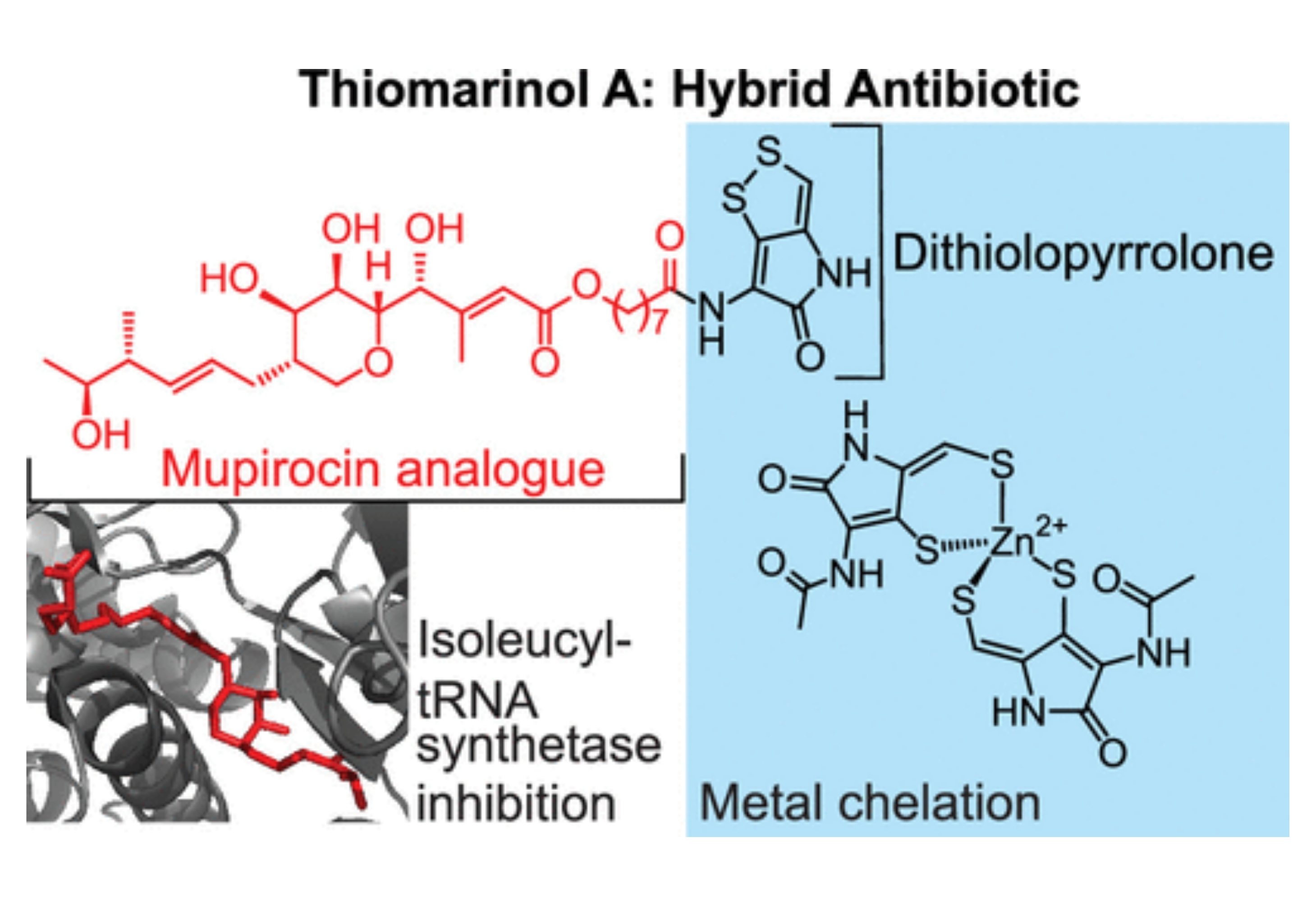
We show that thiomarinol A targets IleRS. A knockdown of the IleRS-encoding gene, ileS, exhibited sensitivity to a synthetic analogue of thiomarinol A in a chemical genomics screen.
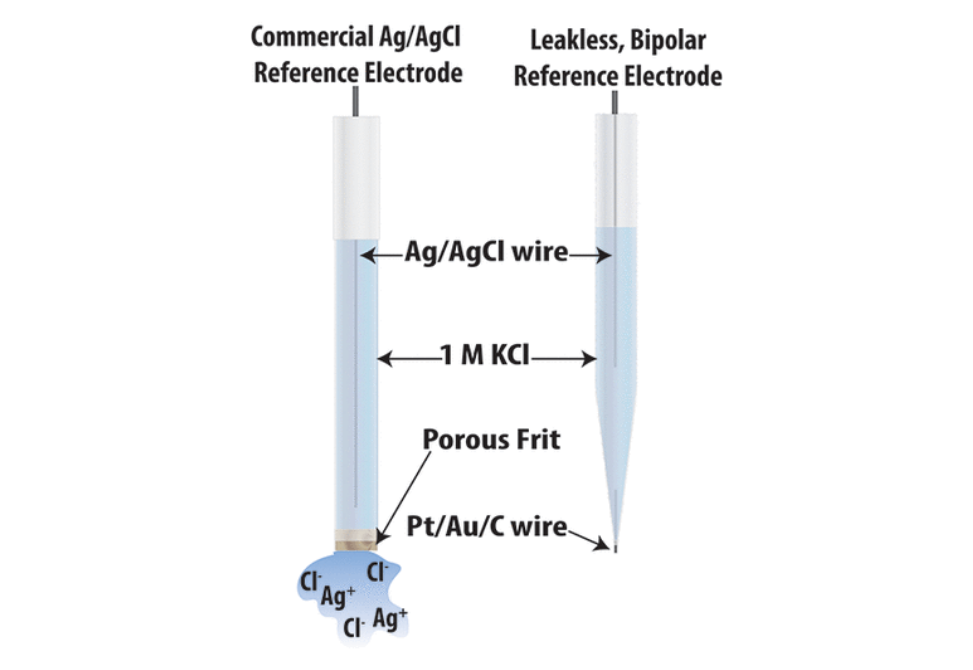
Here, we present an alternative, where the traditional Ag/AgCl reference electrode porous frit is replaced by a conductive wire, preventing ion leakage and allowing miniaturization to the microscale.
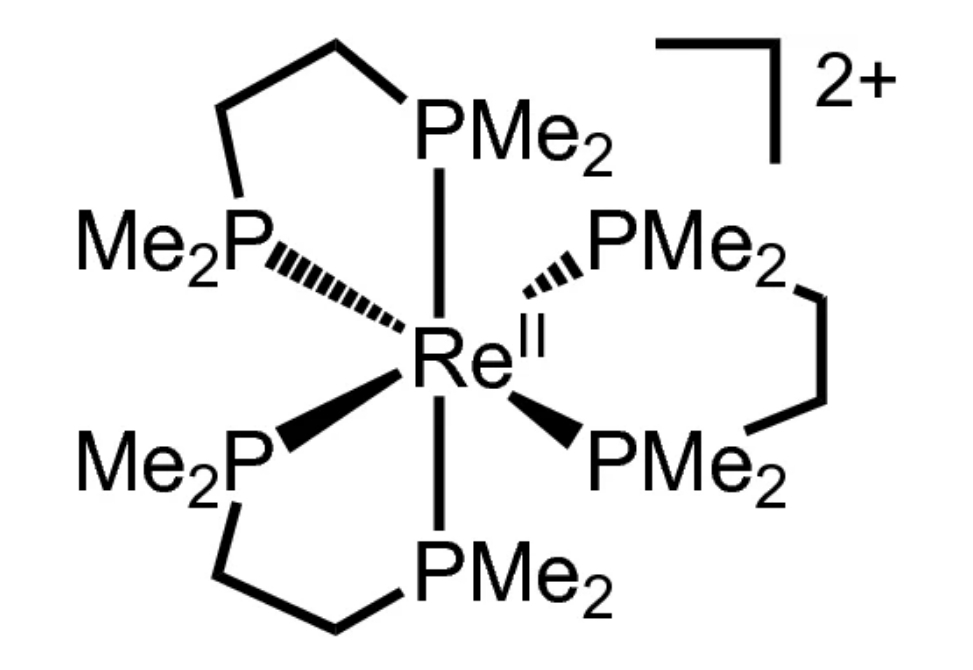
The ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT) transitions of [Re(dmpe)3]2+ (dmpe = bis-1,2-(dimethylphosphino)ethane) were interrogated using UV/Vis absorbance spectroscopy, photoluminescence spectroscopy, and time-dependent density functional theory.
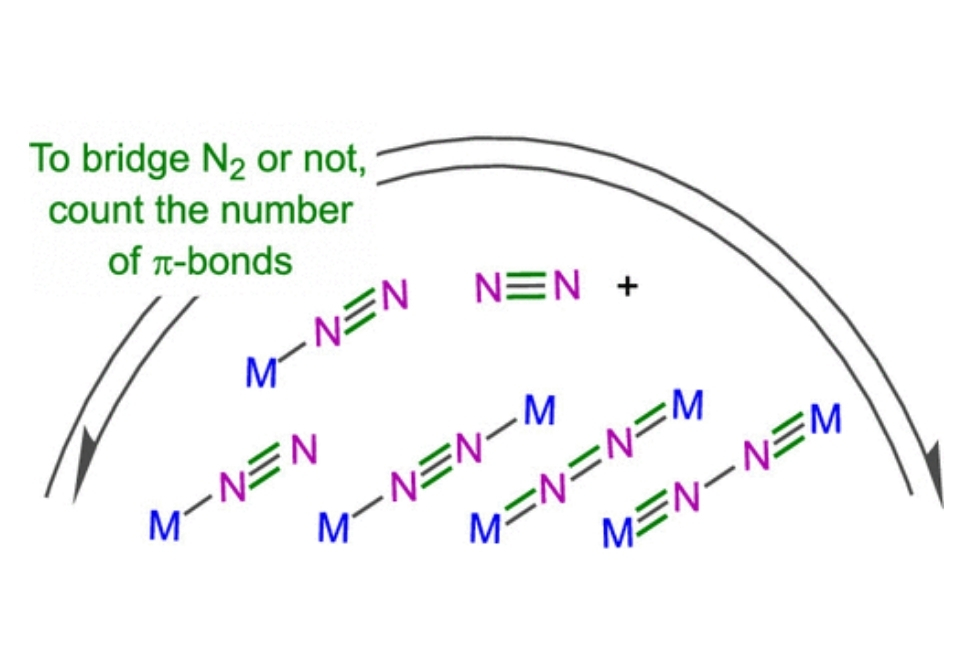
Here we elucidate the fundamental factors controlling the two binding modes and determining which is favored for a given metal–ligand system, using both quantitative density functional theory (DFT) and qualitative molecular orbital (MO) analyses.
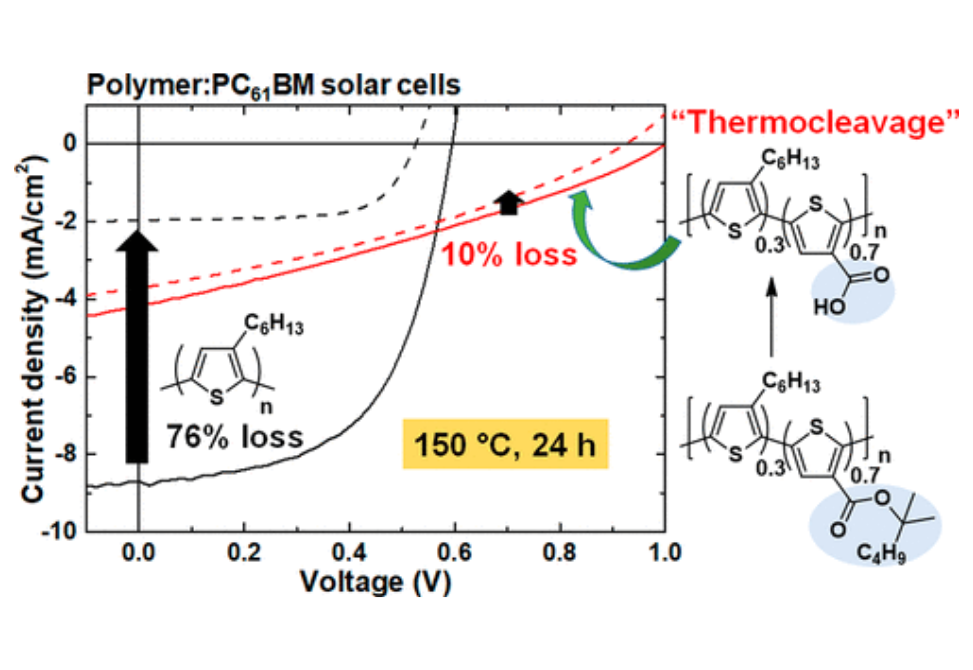
We explore a series of regioregular polythiophenes having TCSs and hexyl side chains by varying the ratio of different side chains, from 0 mol % TCSs to 100 mol % TCSs at an increment of 20 mol %.
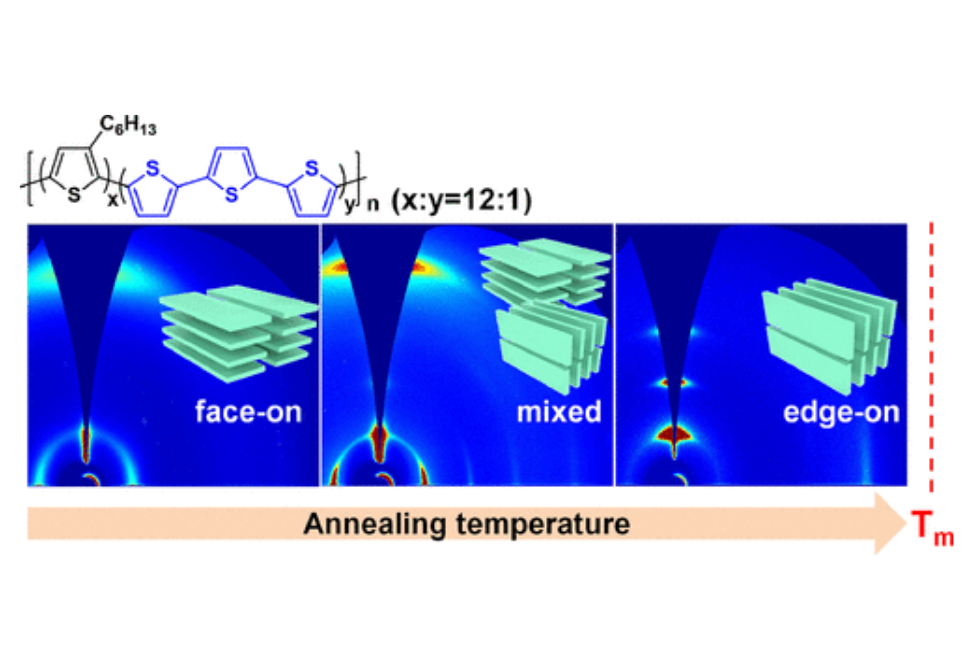
We designed and synthesized a random copolymer (RP-3T) by inserting unsubstituted terthiophenes into regioregular poly(3-hexylthiophene)s.
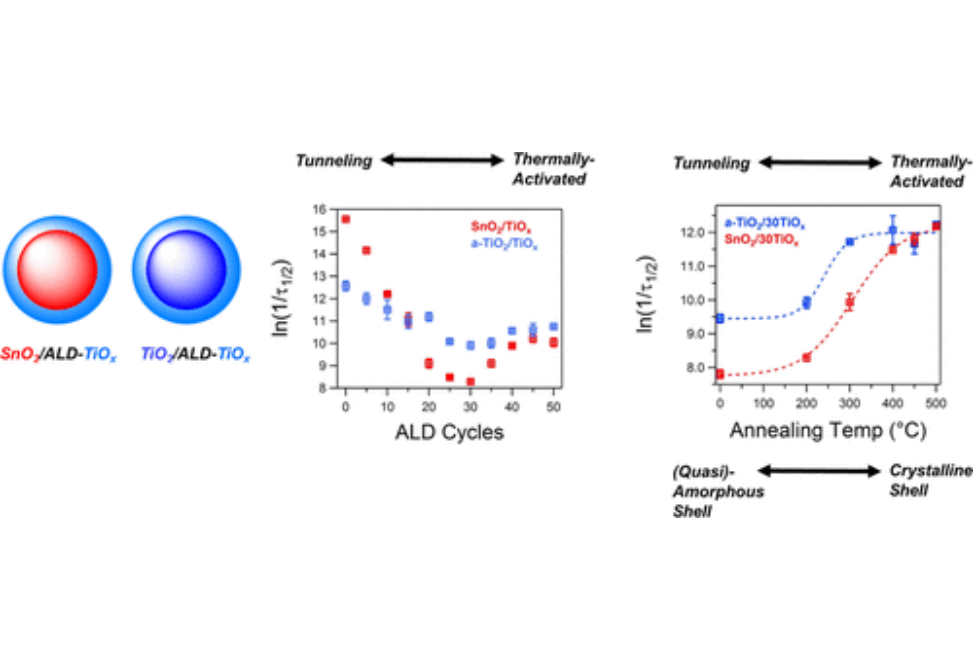
Mesoporous anatase TiO2, mixed anatase/brookite TiO2, and rutile-type SnO2 nanocrystalline films were coated with ultrathin (<5 nm) TiOx by the atomic layer deposition (ALD) of tetrakisdimethylamidotitanium(IV) and water at 150 °C to fabricate SnO2/TiOx and TiO2/TiOx core/shell materials.