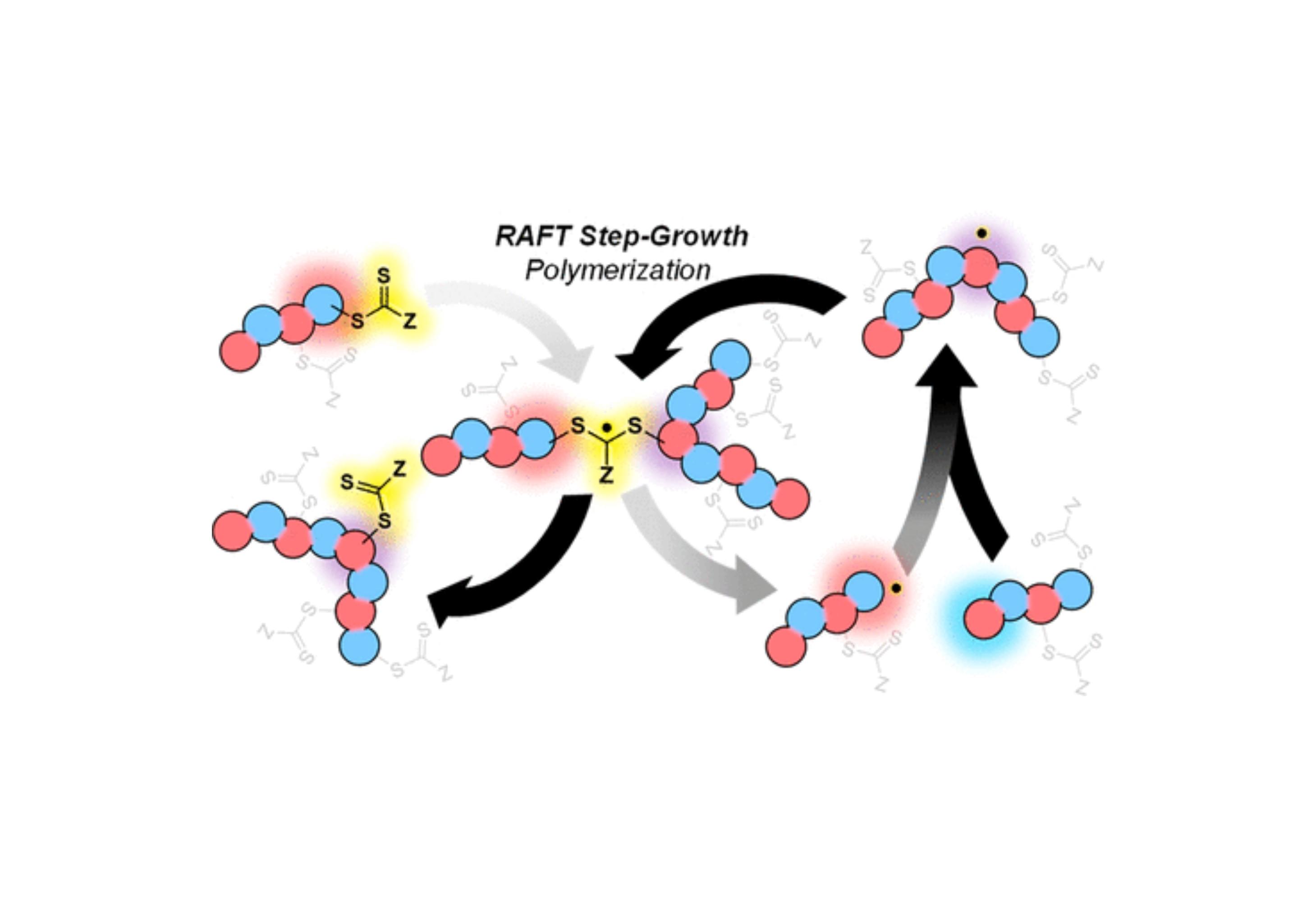
Research Archive
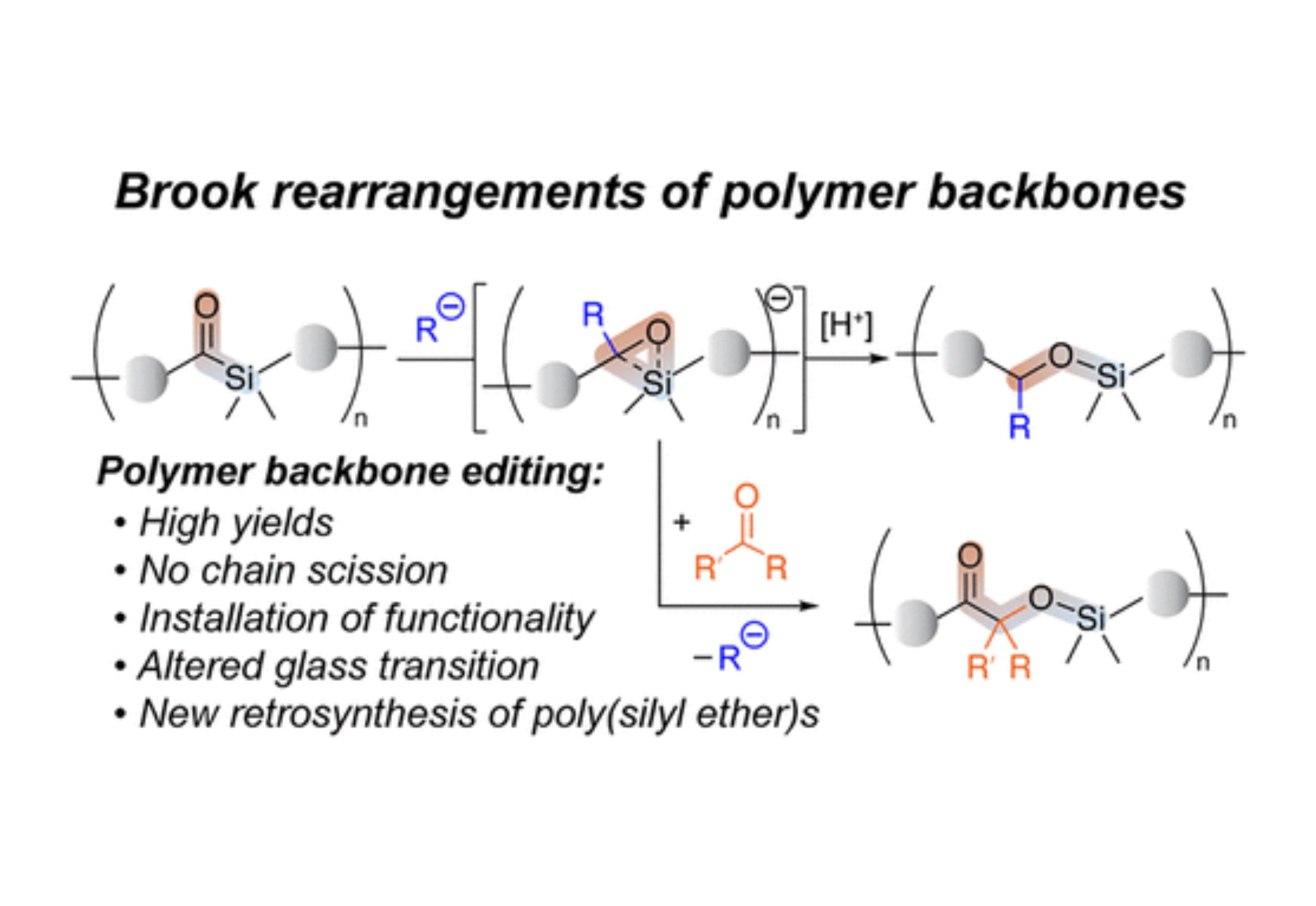
This work demonstrates that poly(silyl ether)s can be derived from poly(acyl silane)s through Brook rearrangements and Brook/benzoin sequences. Such skeletal editing is a powerful strategy to install functionality and modify properties of polymeric materials.
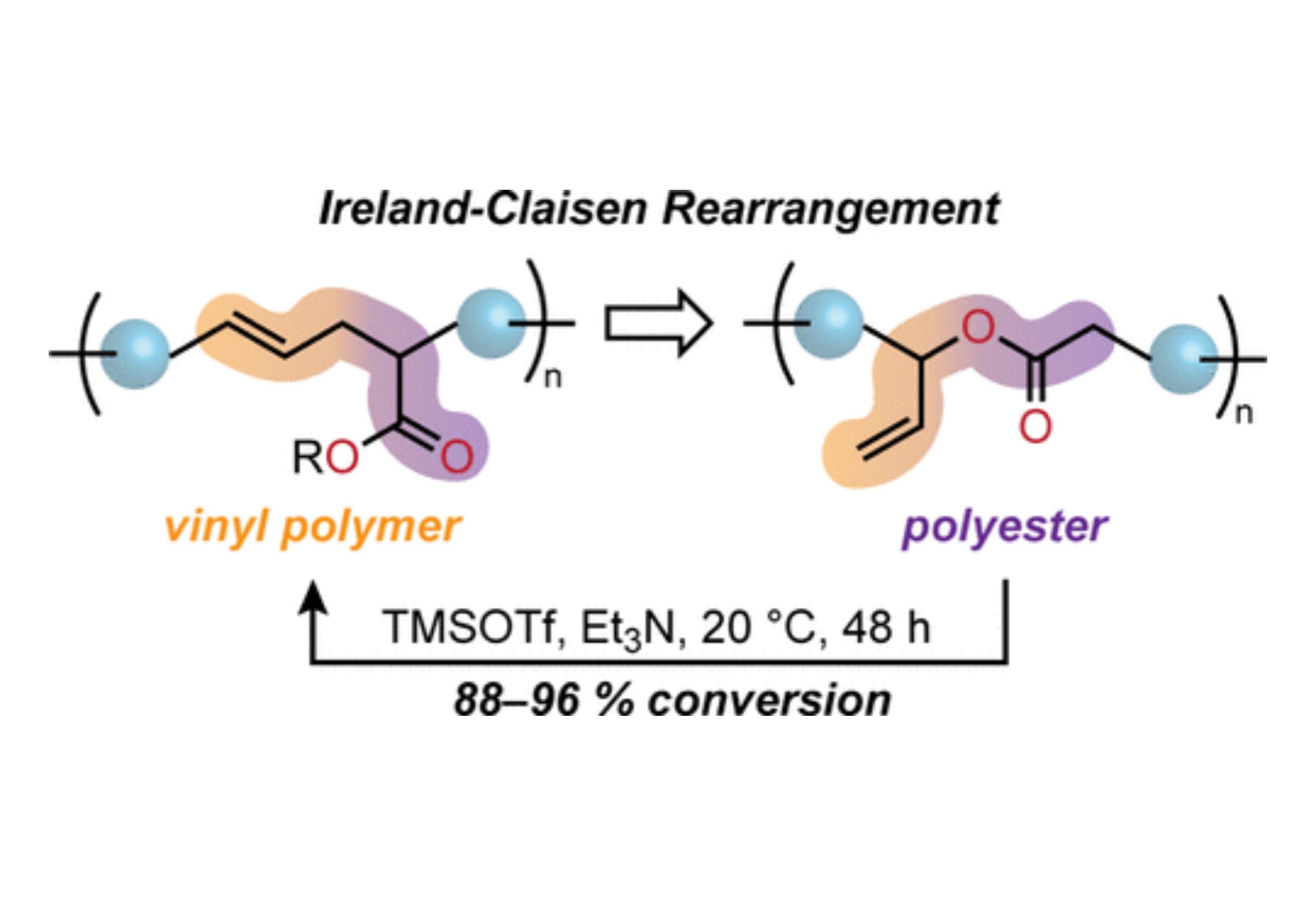
This work demonstrates that industrially-relevant vinyl polymers can be derived from polyesters through a sigmatropic rearrangement. Such editing of the polymer skeleton leads to dramatic changes in the thermal properties of the materials, and provides access to novel polymer compositions and structural precision.
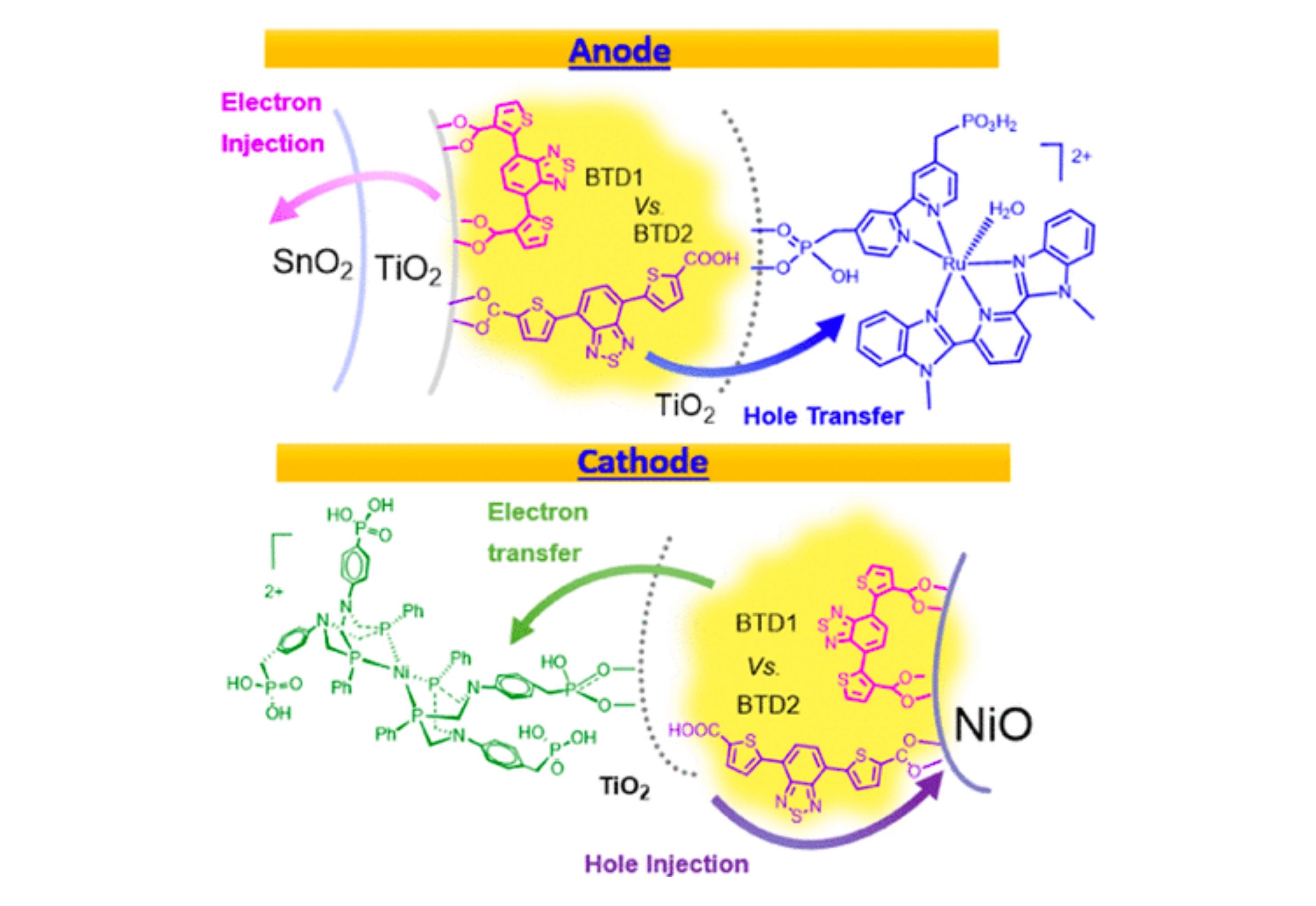
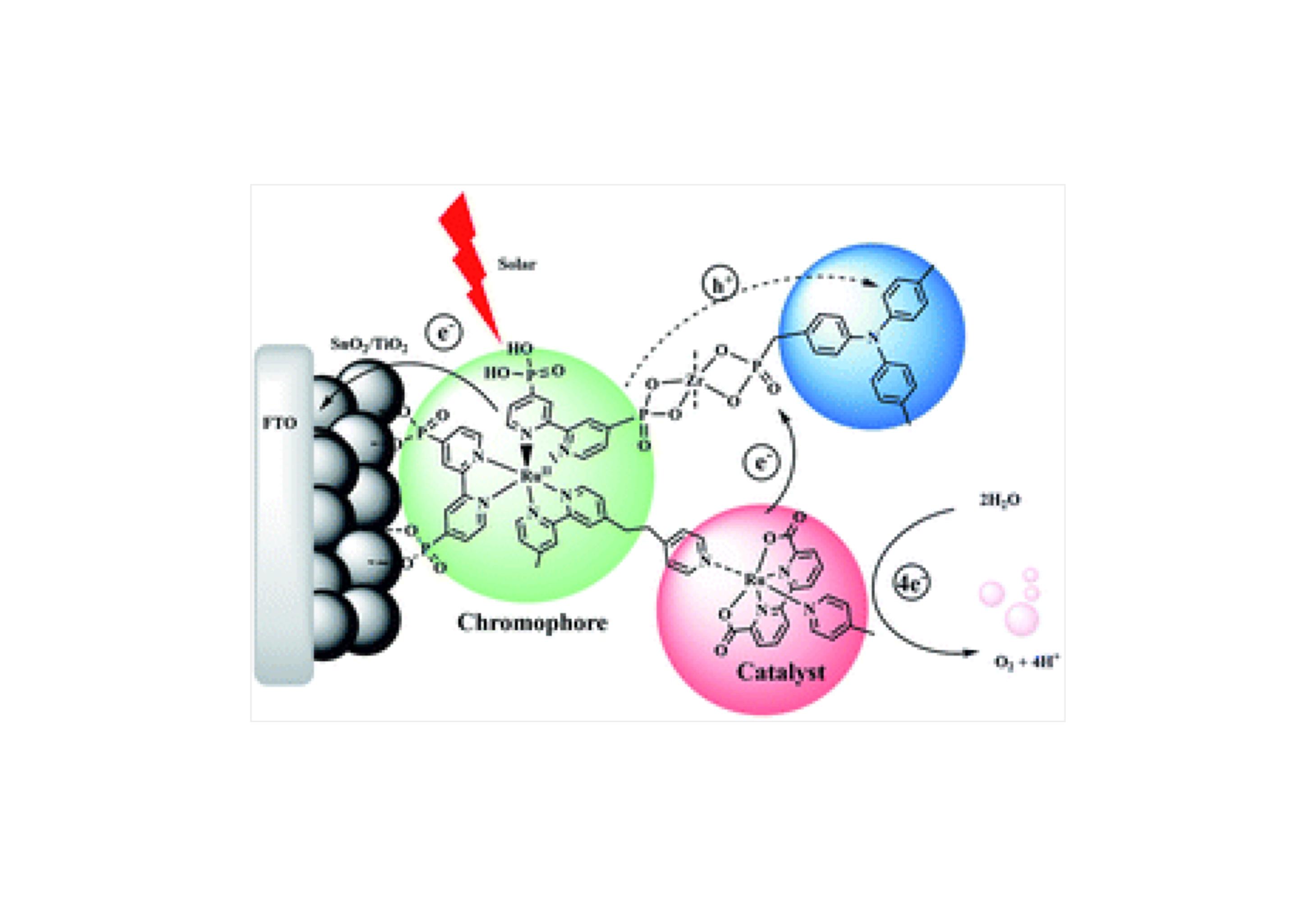
In this work, we compare the optoelectronic properties and photoelectrochemical performance of two D–A–D structural isomers with thiophene-X-carboxylic acid (X denotes 3 and 2 positions) derivatives and 2,1,3-benzothiadiazole as the D and A moieties, respectively.
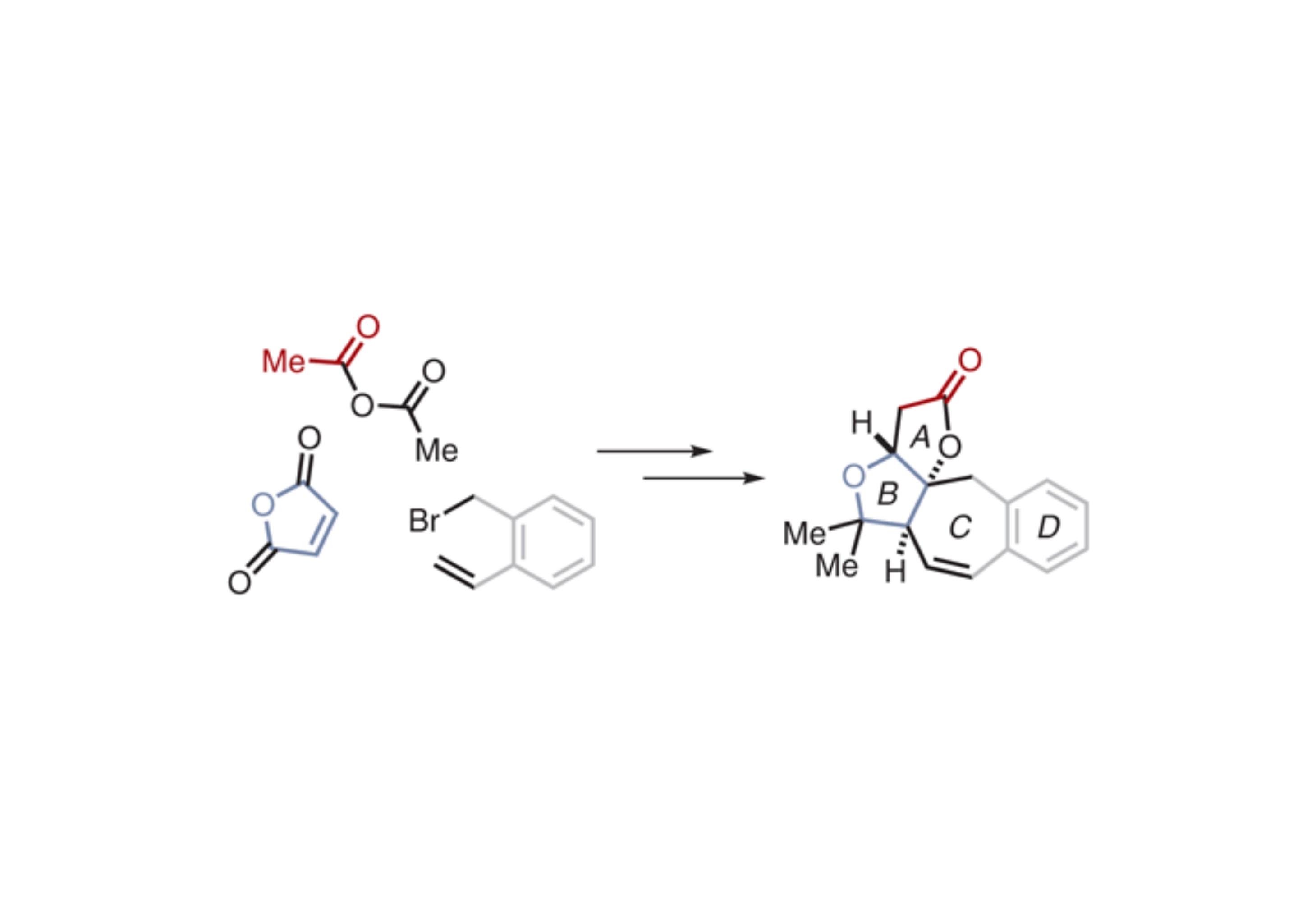
The order in which a ring-closing metathesis and enolate oxidation were performed on this compound dictated the relative stereochemistry of the target.

This review summarizes the advancements in the field over the last decade, encompassing all aspects of the DSC technology: theoretical studies, characterization techniques, materials, applications as solar cells and as drivers for the synthesis of solar fuels, and commercialization efforts from various companies.
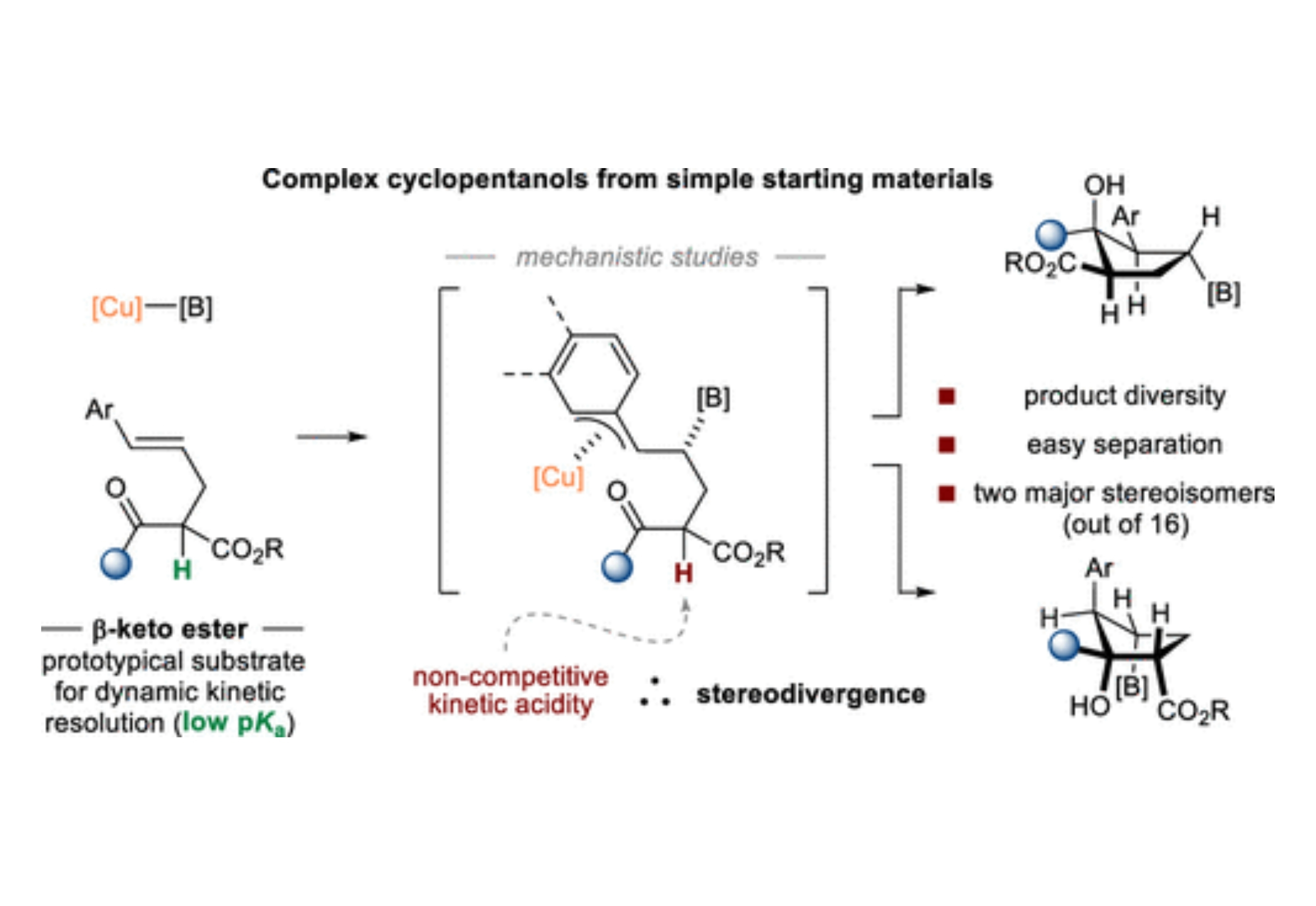
This article describes stereodivergent Cu-catalyzed borylative cyclizations of racemic β-oxo acid derivatives bearing tethered pro-nucleophilic olefins to deliver highly functionalized cyclopentanols containing four contiguous stereogenic centers.
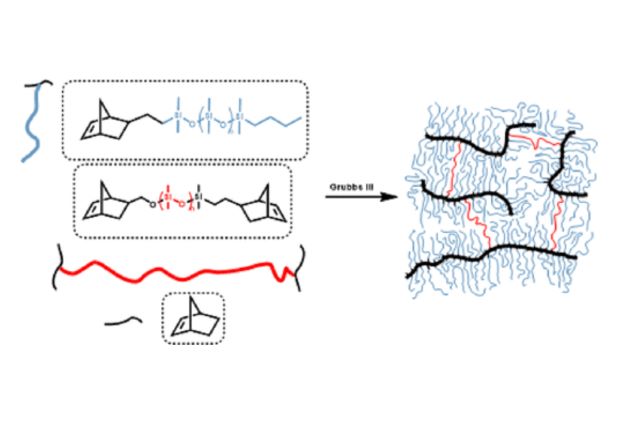
Here, we show that brush elastomers made by ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) of norbornene-terminated poly(dimethylsiloxane) macromonomers are less extensible than brush elastomers with the methacrylate backbone yet not as extensible (λmax) as predicted by the strain-stiffening parameter (β) derived from fitting the experimental stress–strain curves.