Isoprene Epoxydiol-Derived Sulfated and Nonsulfated Oligomers Suppress Particulate Mass Loss during Oxidative Aging of Secondary Organic Aerosol
Abstract
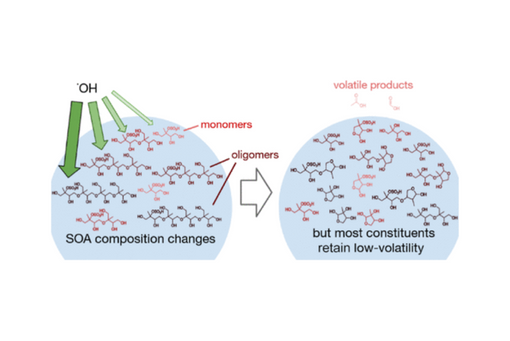
Acid-driven multiphase chemistry of isoprene epoxydiols (IEPOX) with inorganic sulfate aerosols contributes substantially to secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation, which constitutes a large mass fraction of atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5). However, the atmospheric chemical sinks of freshly generated IEPOX-SOA particles remain unclear. We examined the role of heterogeneous oxidation of freshly generated IEPOX-SOA particles by gas-phase hydroxyl radical (•OH) under dark conditions as one potential atmospheric sink. After 4 h of gas-phase •OH exposure (∼3 × 108 molecules cm–3), chemical changes in smog chamber-generated IEPOX-SOA particles were assessed by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization high-resolution quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HILIC/ESI-HR-QTOFMS). A comparison of the molecular-level compositional changes in IEPOX-SOA particles during aging with or without •OH revealed that decomposition of oligomers by heterogeneous •OH oxidation acts as a sink for •OH and maintains a reservoir of low-volatility compounds, including monomeric sulfate esters and oligomer fragments. We propose tentative structures and formation mechanisms for previously uncharacterized SOA constituents in PM2.5. Our results suggest that this •OH-driven renewal of low-volatility products may extend the atmospheric lifetimes of particle-phase IEPOX-SOA by slowing the production of low-molecular weight, high-volatility organic fragments and likely contributes to the large quantities of 2-methyltetrols and methyltetrol sulfates reported in PM2.5.
Citation
Isoprene Epoxydiol-Derived Sulfated and Nonsulfated Oligomers Suppress Particulate Mass Loss during Oxidative Aging of Secondary Organic Aerosol
N. Cazimir Armstrong, Yuzhi Chen, Tianqu Cui, Yue Zhang, Cade Christensen, Zhenfa Zhang, Barbara J. Turpin, Man Nin Chan, Avram Gold, Andrew P. Ault, and Jason D. Surratt
Environmental Science & Technology 2022 56 (23), 16611-16620
DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.2c03200