Brønsted Acid Catalyzed Stereoselective Polymerization of Vinyl Ethers
Abstract
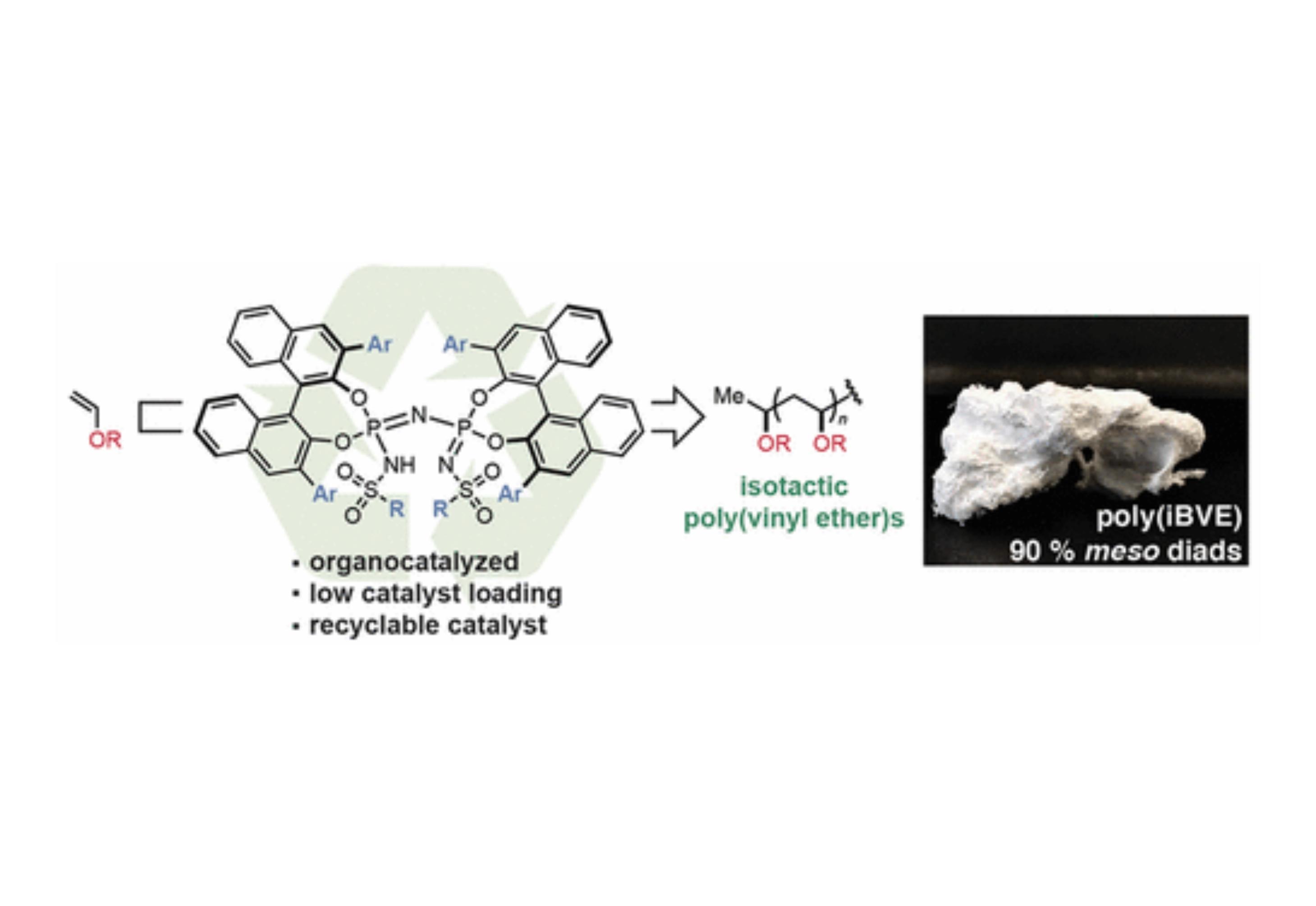
Isotactic poly(vinyl ether)s (PVEs) have recently been identified as a new class of semicrystalline thermoplastics with a valuable combination of mechanical and interfacial properties. Currently, methods to synthesize isotactic PVEs are limited to strong Lewis acids that require a high catalyst loading and limit the accessible scope of monomer substrates for polymerization. Here, we demonstrate the first Brønsted acid catalyzed stereoselective polymerization of vinyl ethers. A single-component imidodiphosphorimidate catalyst exhibits a sufficiently low pKa to initiate vinyl ether polymerization and acts as a chiral conjugate base to direct the stereochemistry of monomer addition to the oxocarbenium ion reactive chain end. This Brønsted acid catalyzed stereoselective polymerization enabled an expanded substrate scope compared to previous methods, the use of chain transfer agents to lower catalyst loading, and the capability to recycle the catalyst for multiple polymerizations.
Citation
Brønsted Acid Catalyzed Stereoselective Polymerization of Vinyl Ethers
Phil C. Knutson, Aaron J. Teator, Travis P. Varner, Caleb T. Kozuszek, Paige E. Jacky, and Frank A. Leibfarth
Journal of the American Chemical Society 2021 143 (40), 16388-16393
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c08282