Tyrosinase-Catalyzed Peptide Macrocyclization for mRNA Display
Abstract
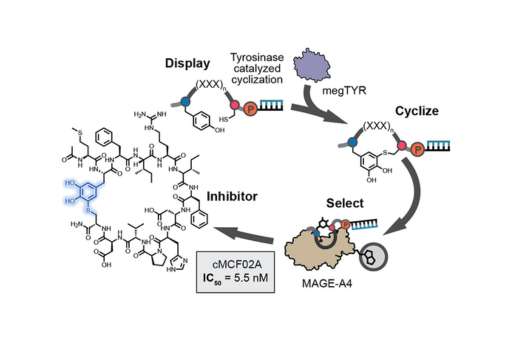
mRNA display of macrocyclic peptides has proven itself to be a powerful technique to discover high-affinity ligands for a protein target. However, only a limited number of cyclization chemistries are known to be compatible with mRNA display. Tyrosinase is a copper-dependent oxidase that oxidizes tyrosine phenol to an electrophilic o-quinone, which is readily attacked by cysteine thiol. Here we show that peptides containing tyrosine and cysteine are rapidly cyclized upon tyrosinase treatment. Characterization of the cyclization reveals it to be widely applicable to multiple macrocycle sizes and scaffolds. We combine tyrosinase-mediated cyclization with mRNA display to discover new macrocyclic ligands targeting melanoma-associated antigen A4 (MAGE-A4). These macrocycles potently inhibit the MAGE-A4 binding axis with nanomolar IC50 values. Importantly, macrocyclic ligands show clear advantage over noncyclized analogues with ∼40-fold or greater decrease in IC50 values.
Citation
Tyrosinase-Catalyzed Peptide Macrocyclization for mRNA Display
Matthew C. Fleming, Matthew M. Bowler, Rodney Park, Konstantin I. Popov, and Albert A. Bowers
Journal of the American Chemical Society 2023 145 (19), 10445-10450
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c12629