Carbazole-Based Hole Transport Polymer for Methylammonium-Free Tin–Lead Perovskite Solar Cells with Enhanced Efficiency and Stability
Abstract
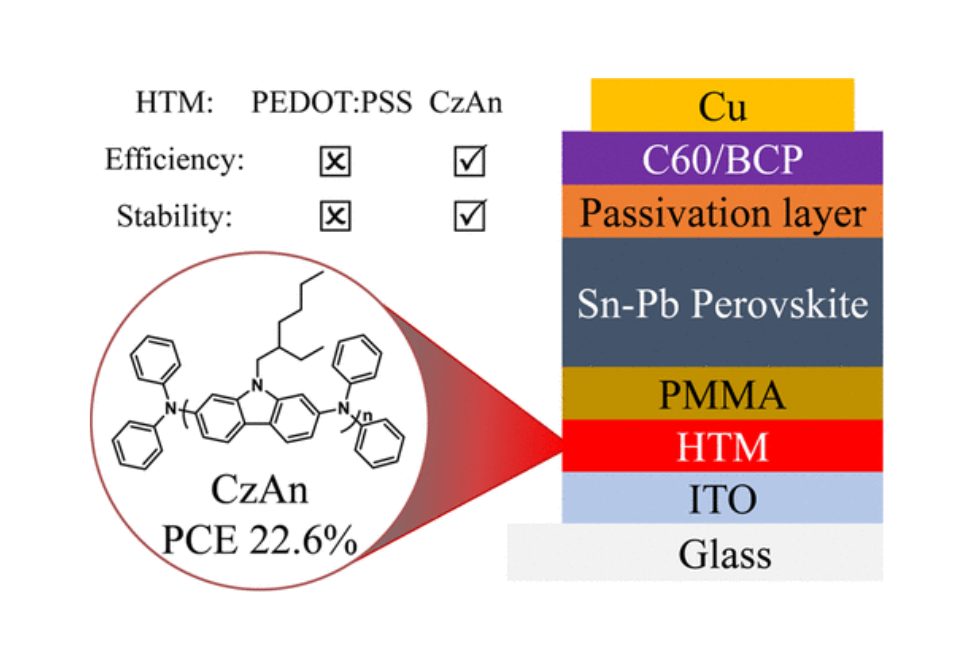
As the most commonly used hole transport material (HTM) in tin–lead (Sn–Pb) perovskite solar cells (PSCs), poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrenesulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) limits the power conversion efficiency (PCE) and stability of the PSCs due to its acidic characteristics. Herein, an easily synthesized polymer HTM poly[(phenyl)imino[9-(2-ethylhexyl)carbazole]-2,7-diyl] (CzAn) with a shallow highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) level of −4.95 eV is used in a p-i-n structure, methylammonium-free, Sn–Pb PSC to replace PEDOT:PSS. Upon optimization using doping and surface engineering, high quality Sn–Pb PSCs could be successfully fabricated, boosting the PCE to 22.6% (stabilized PCE of 21.3%) compared with 21.2% for PEDOT:PSS. The perovskite films prepared on the modified CzAn HTM possess improved crystallinity, reduced trap-state density, and larger carrier mobility resulting in PSCs with greatly improved stability.
Citation
Carbazole-Based Hole Transport Polymer for Methylammonium-Free Tin–Lead Perovskite Solar Cells with Enhanced Efficiency and Stability
Jiantao Wang, Zhenhua Yu, Daniel D. Astridge, Zhenyi Ni, Liang Zhao, Bo Chen, Mengru Wang, Ying Zhou, Guang Yang, Xuezeng Dai, Alan Sellinger, and Jinsong Huang
ACS Energy Letters 2022 7 (10), 3353-3361
DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.2c01578