Achieving Site-Selective C-O Bond Reduction for High-Value Cellulosic Valorization
Abstract
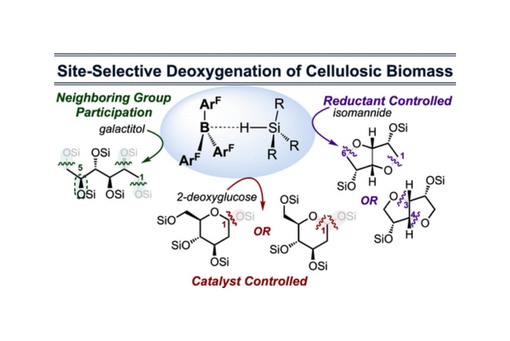
This perspective describes key lessons from a program whose goals are to site-selectively deoxygenate cellulose-derived carbohydrates. By focusing on noneliminative mechanisms, the loss of stereochemistry in the products is minimized, which inherently retains/creates value. Fluoroaryl borane catalysts are uniquely capable of hydrosilane heterolytic activation and, in the sugar context, facilitate the neighboring group participation and intermediacy of silyl-oxonium ions prior to reduction that drives selectivity. Methods for substrate and catalyst control over the site and extent of deoxygenation are critical outcomes, though lessons learned from catalysis in high-density environments apply to important problems in catalysis and selectivity.
Citation
Clarke, J., Seo, Y., Gagné, M. R., & Bender, T. A. (2022). Achieving site-selective C–O bond reduction for high-value cellulosic valorization. ACS Catalysis, 12(22), 14220–14226. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.2c04768