Research Archive
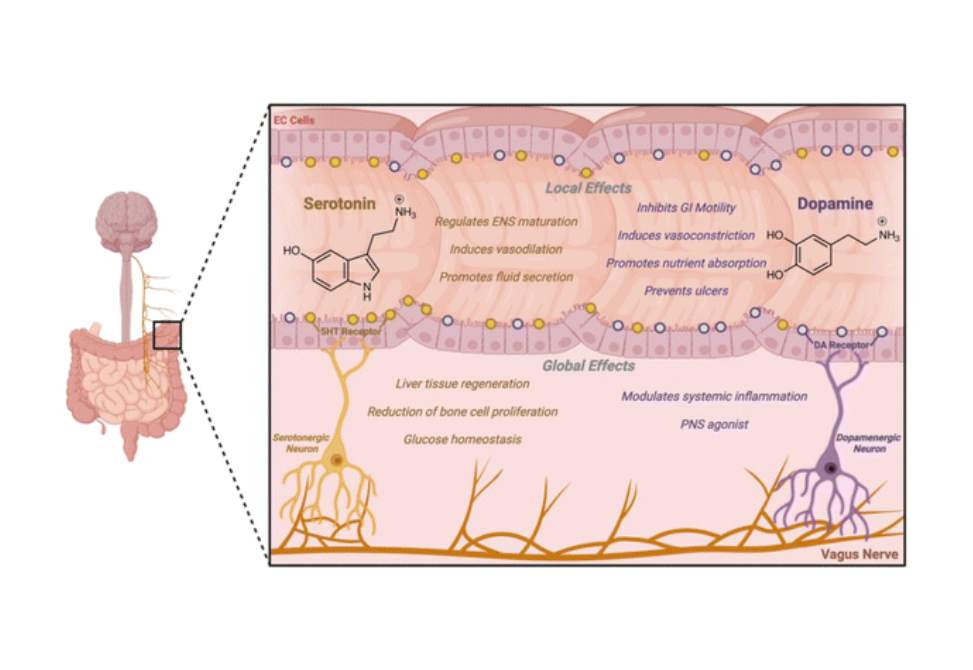
Here we review foundational studies that defined molecular relationships between the microbiota, neurotransmitters, and the gut-brain axis.
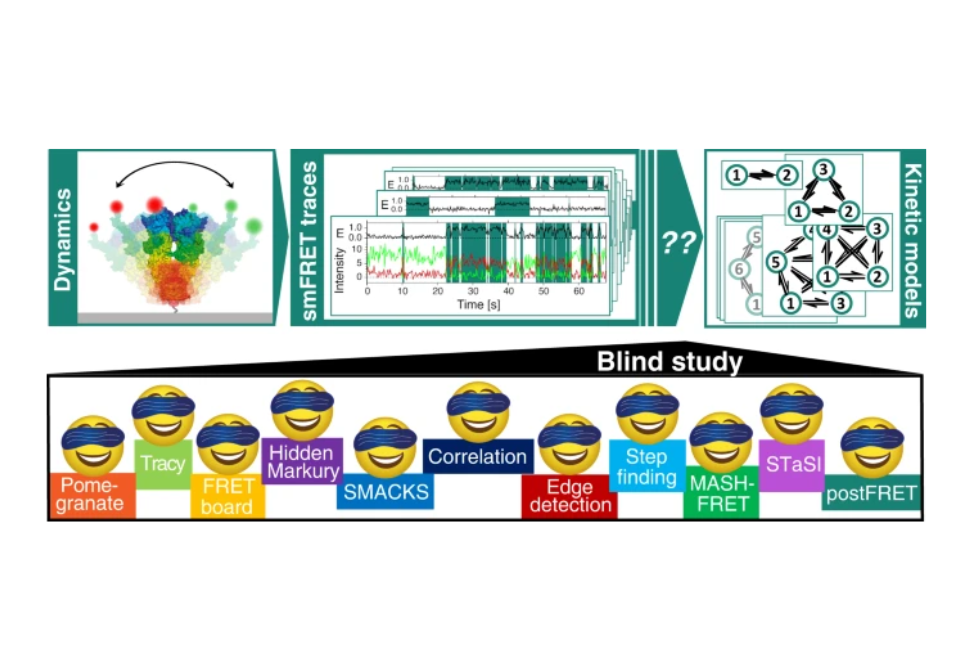
Here, we report the results of a blind benchmark study assessing eleven analysis tools used to infer kinetic rate constants from smFRET trajectories.
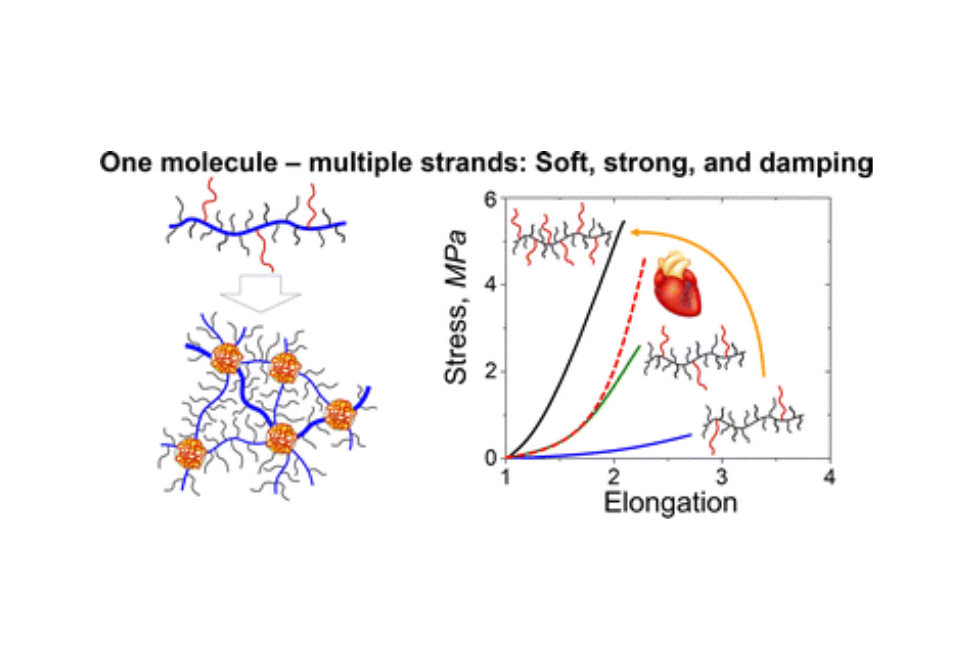
Herein, we present the A-g-B brush-like graft copolymer platform as a framework for fabrication of materials with independently tunable softness and firmness, capable of reaching a strength of ∼10 MPa on par with stress-supporting tissues such as blood vessel, muscle, and skin.
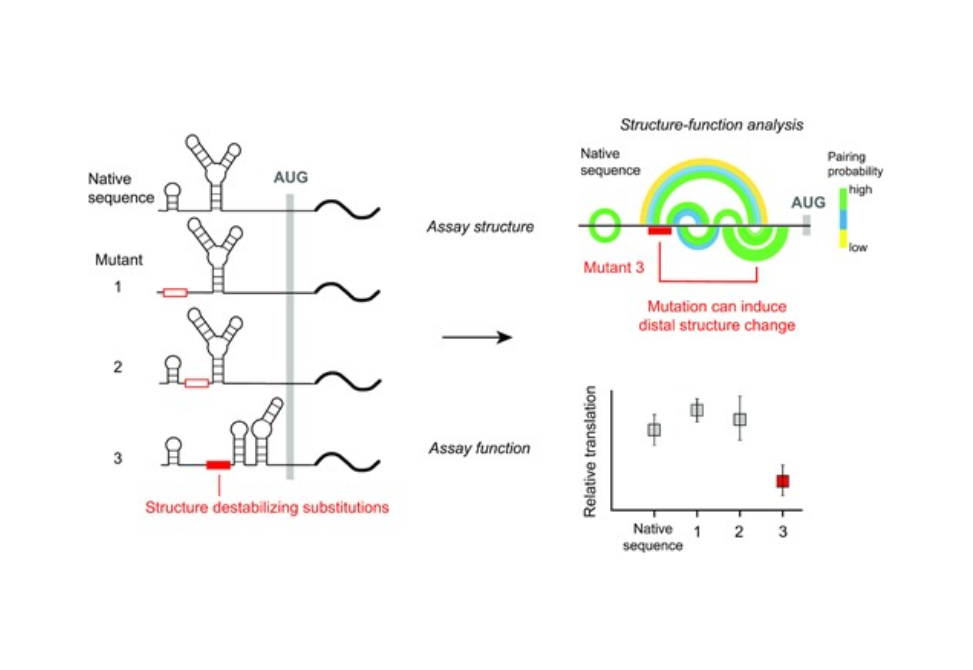
We show that the 5′-UTR of NM_000295.4 folds into a well-defined multi-helix structural domain. We systematically destabilized mRNA structure across the NM_000295.4 5′-UTR, and measured changes in (SHAPE quantified) RNA structure and cap-dependent translation relative to a native-sequence reporter.
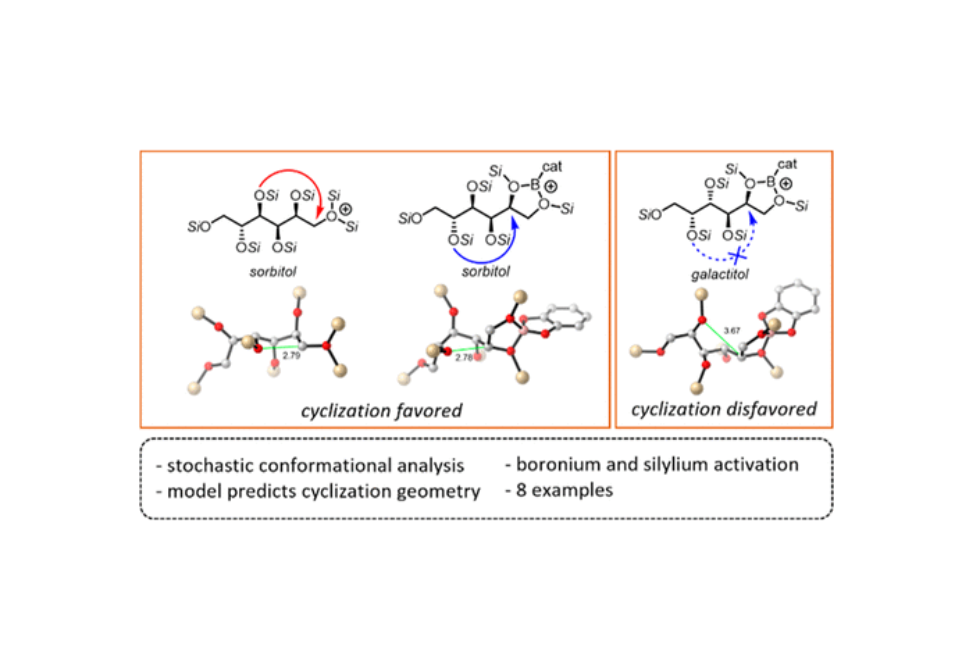
The condensative cyclization of sp3 C–O bonds in per-silylated hexitols is investigated by computation.
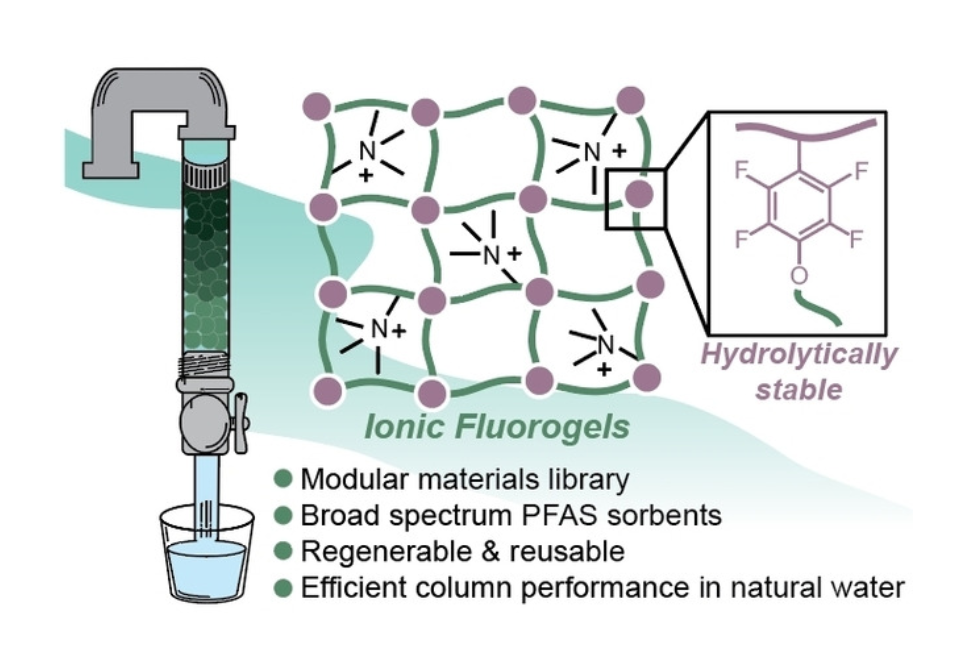
Herein, we report a class of polymer networks with a synergistic combination of ionic and fluorous components that serve as granular materials for the removal of anionic PFAS from water.
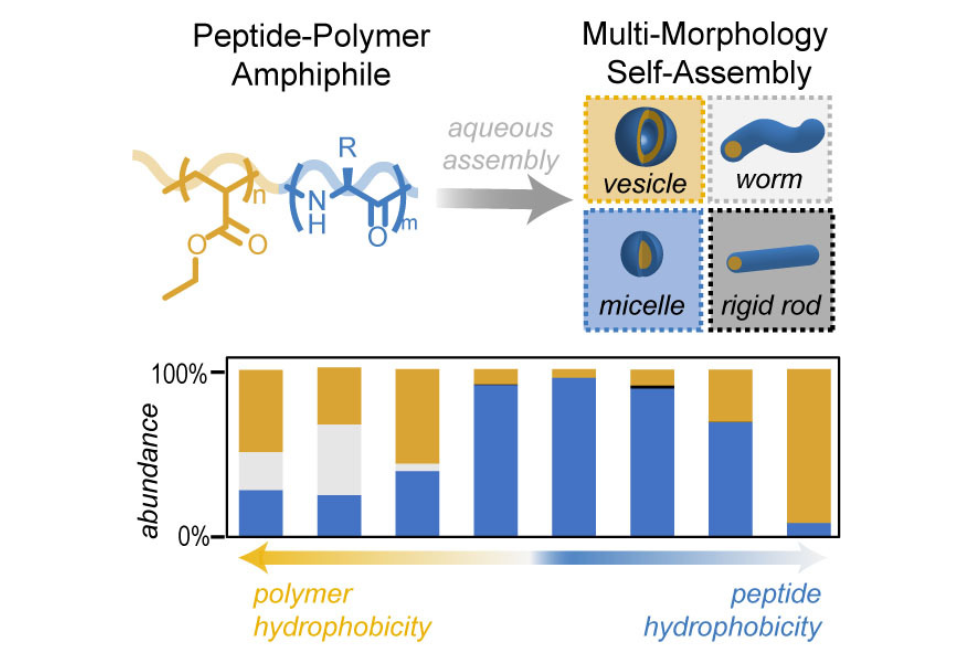
We herein present a systematic study of PPA structure-assembly relationships. PPAs containing oligo(ethyl acrylate) and random-coil peptides were used to determine the role of oligomer molecular weight, dispersity, peptide length, and charge density on self-assembly.
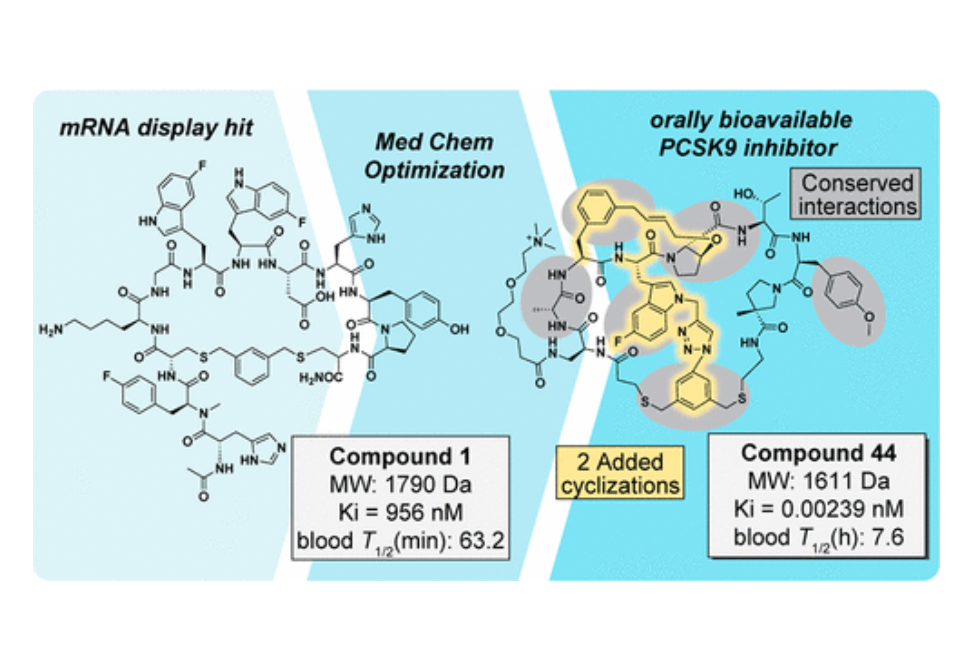
Herein, we discuss the chemical and pharmacological challenges surmounted in bringing this compound to trials and the current outlook for mRNA display-based therapeutic development.
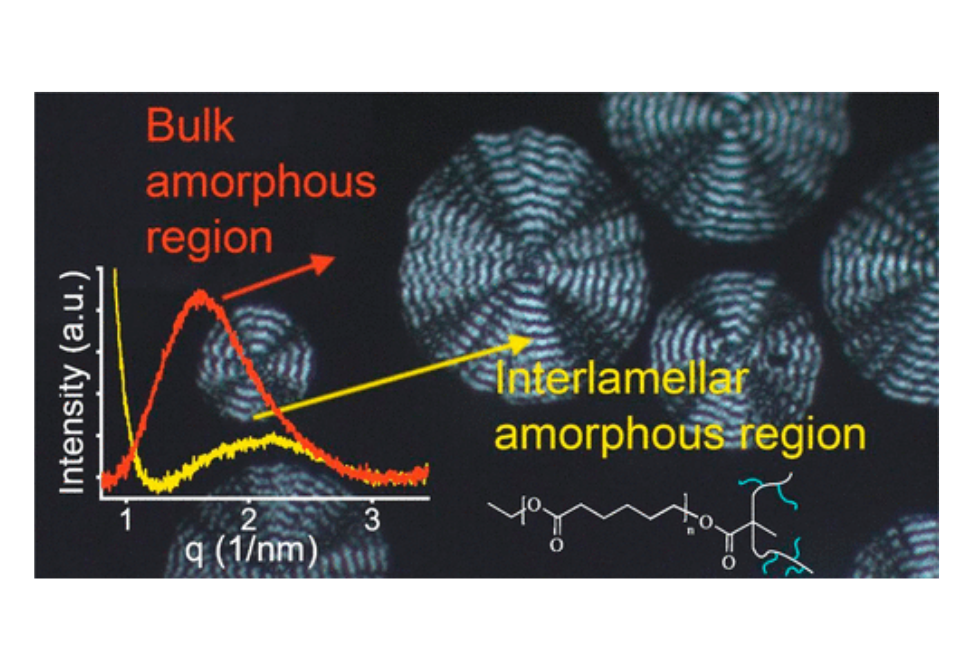
To understand the transition between the two states, the crystallization process was studied with synchrotron X-ray scattering for a series of brush elastomers with poly(ε-caprolactone) side chains bearing from 7 to 13 repeat units.
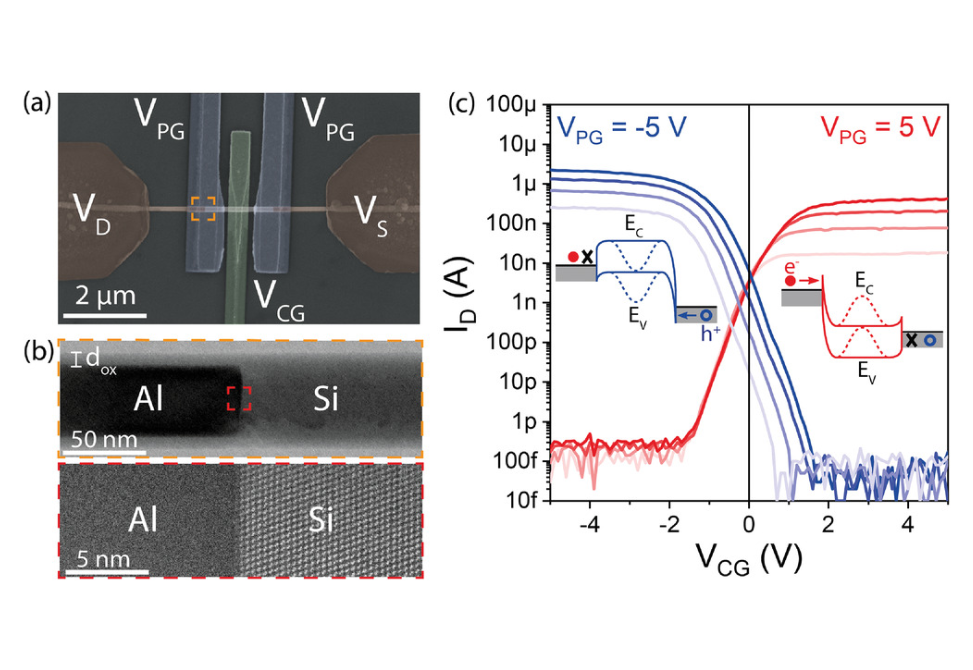
Targeting the enhancement of fabrication reproducibility and electrical balancing between operation modes, here a nanoscale Al-Si-Al nanowire heterostructure with single elementary, monocrystalline Al leads and sharp Schottky junctions is implemented.