Morphology and Viscosity Changes after Reactive Uptake of Isoprene Epoxydiols in Submicrometer Phase Separated Particles with Secondary Organic Aerosol Formed from Different Volatile Organic Compounds
Abstract
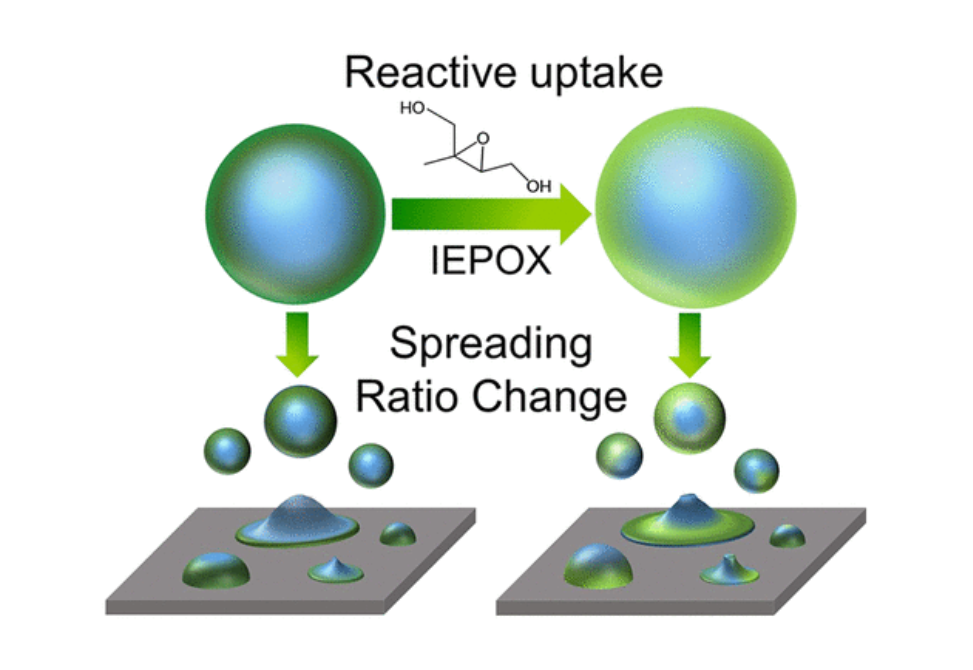
Secondary organic aerosol (SOA), formed from the oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), is a large contributor to atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and is commonly present in mixed inorganic–organic submicron particles. SOA formed from varying biogenic and anthropogenic VOCs results in unique aerosol physicochemical properties that modify climate impacts (i.e., water uptake). Understanding reactive uptake of VOC-derived semivolatile oxidation products to inorganic-SOA mixed particles remains limited, particularly for particles at the most abundant sizes (by number) in the atmosphere (∼100 nm). These particles are challenging to study as SOA can be quite viscous (i.e., solid or semisolid), and mixed particles can have complex morphologies (e.g., core–shell). Herein, we show that the viscosity and morphology of initially core–shell (inorganic–organic) particles changed substantially after acid-catalyzed reactive uptake of isoprene epoxydiols (IEPOX), and that differences were highly dependent on VOC precursor (α-pinene, β-caryophyllene, isoprene, and toluene). SOA from two higher molecular weight precursors (α-pinene and β-caryophyllene) were less viscous after IEPOX uptake at 50% relative humidity (RH), while SOA viscosities from lower molecular weight precursors (isoprene and toluene) did not change appreciably, based on atomic force microscopy (AFM) measurements. The evolution of inorganic-SOA particle viscosity and morphology could alter the predicted impacts of SOA on air quality and climate.
Citation
Morphology and Viscosity Changes after Reactive Uptake of Isoprene Epoxydiols in Submicrometer Phase Separated Particles with Secondary Organic Aerosol Formed from Different Volatile Organic Compounds
DOI: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.1c00156