Research Archive

Herein, an approach for discriminating between tardigrade morphological states is developed and utilized to compare sucrose- and CaCl2-induced tuns, using the model species Hypsibius exemplaris.

Herein, we disclose a backbone rearrangement approach to tune the short-chain branching of polymers.

A new homoleptic Ru polypyridyl complex bearing two aldehyde groups on each bipyridine ligand, [Ru(dab)3](PF6)2, where dab is 4,4′-dicarbaldehyde-2,2′-bipyridine, was synthesized, characterized, and utilized for iodide photo-oxidation studies.

Herein, state-of-the-art research on light-induced electron transfer and cage escape that has appeared since the seminal 1972 review by J. P. Lorand entitled “The Cage Effect” is reviewed.
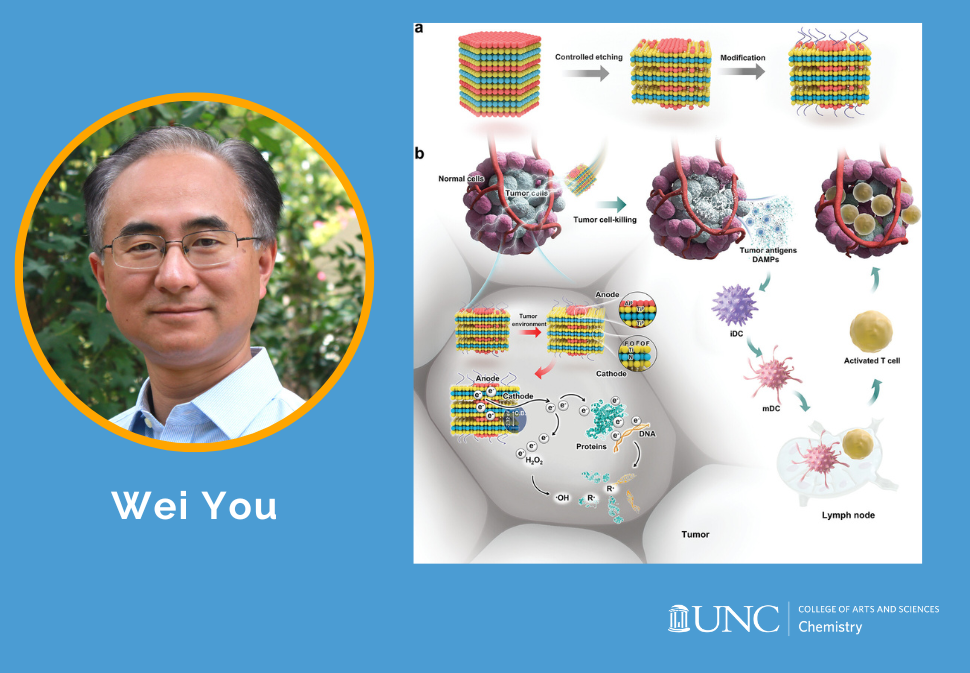
Here, this work presents galvanic cell nanomaterials that can directly release highly reactive electrons in tumors without external irradiation or photosensitizers.
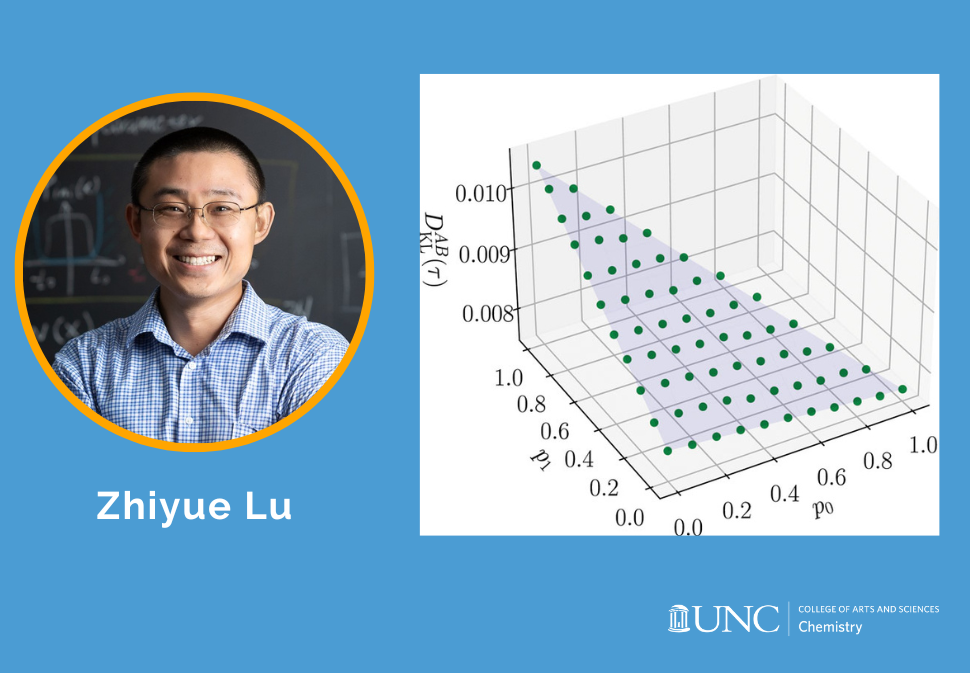
This work provides a general formula that decomposes the Kullback-Leibler divergence in space and time for any Markov processes, arbitrarily far from equilibrium or steady state.
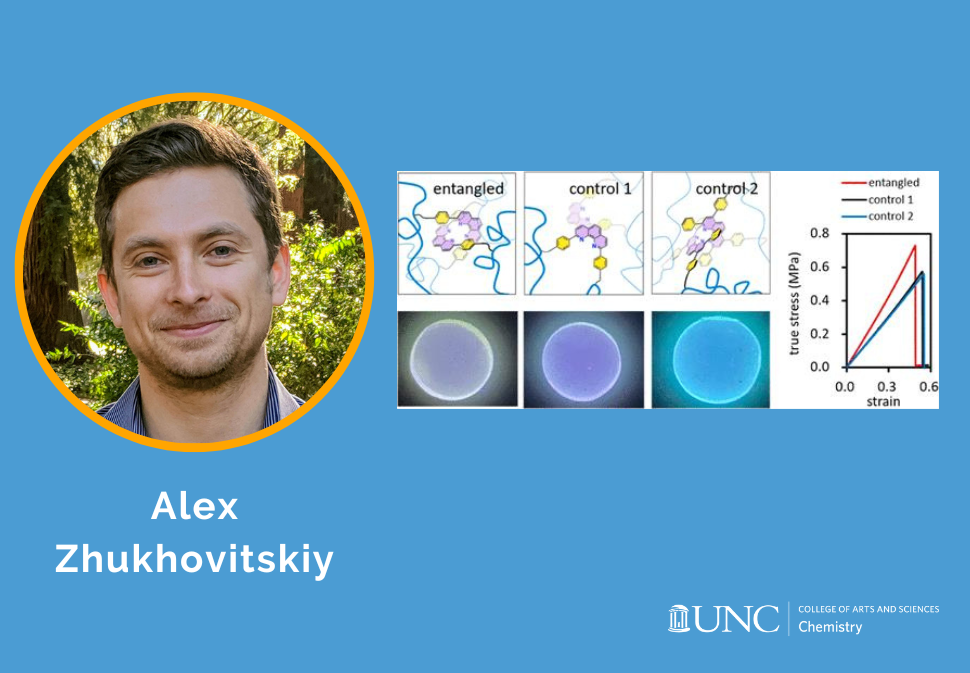
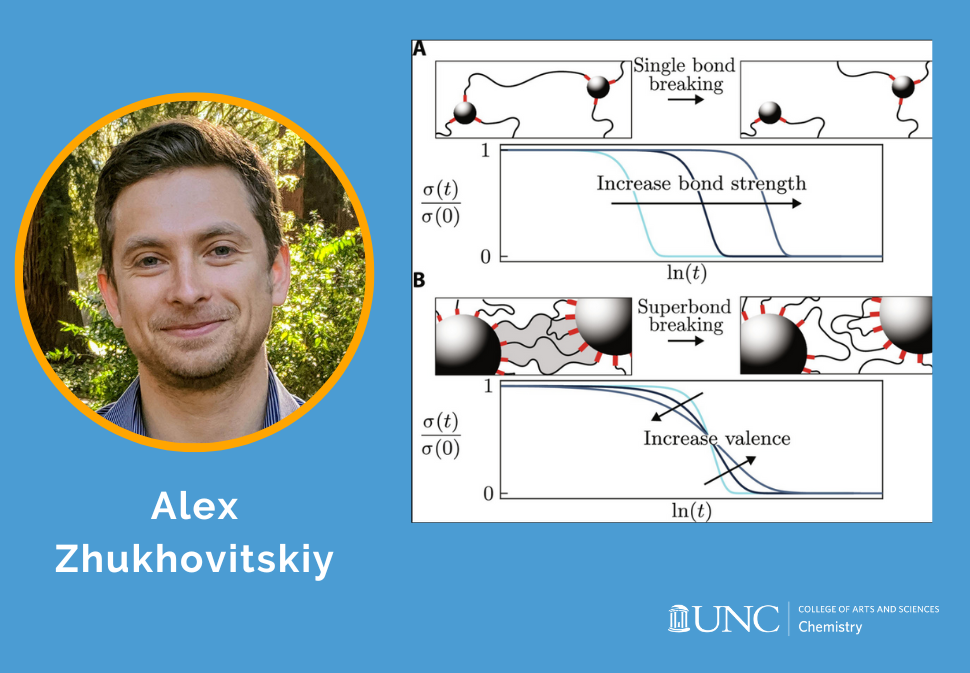
Here, we use supramolecular templates based on phenanthroline-copper(I) complexes to install into poly(methoxyethyl acrylate) elastomer-trapped entanglements whose topology is programmed by the complex geometry.
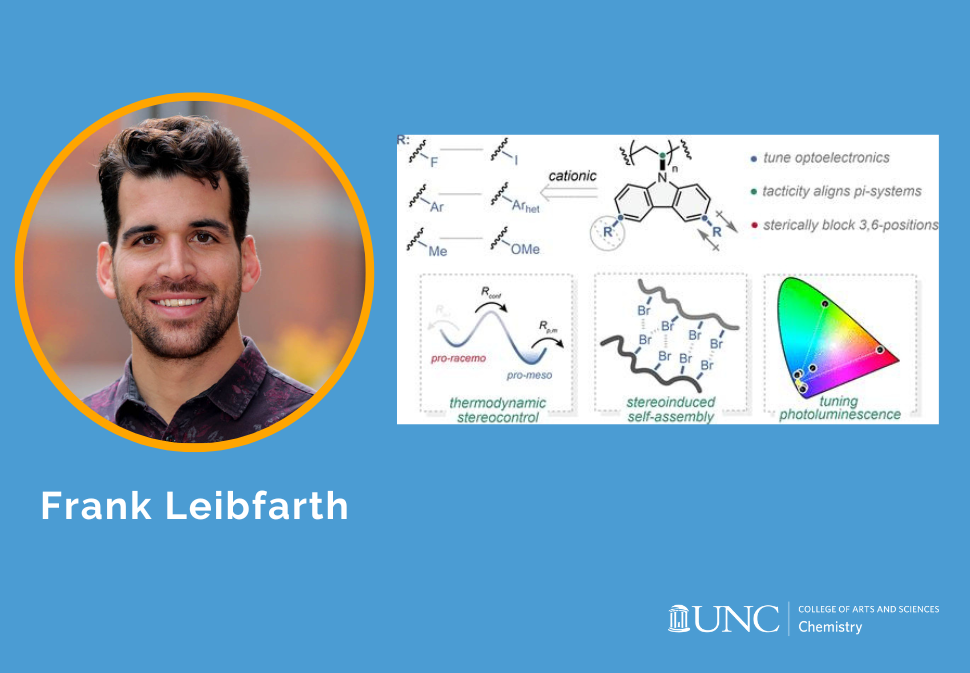
Here, we report the stereoselective cationic polymerization of a series of 3,6-disubtituted N-vinylcarbazole derivatives using a chiral scandium-bis(oxazoline) Lewis acid catalyst.
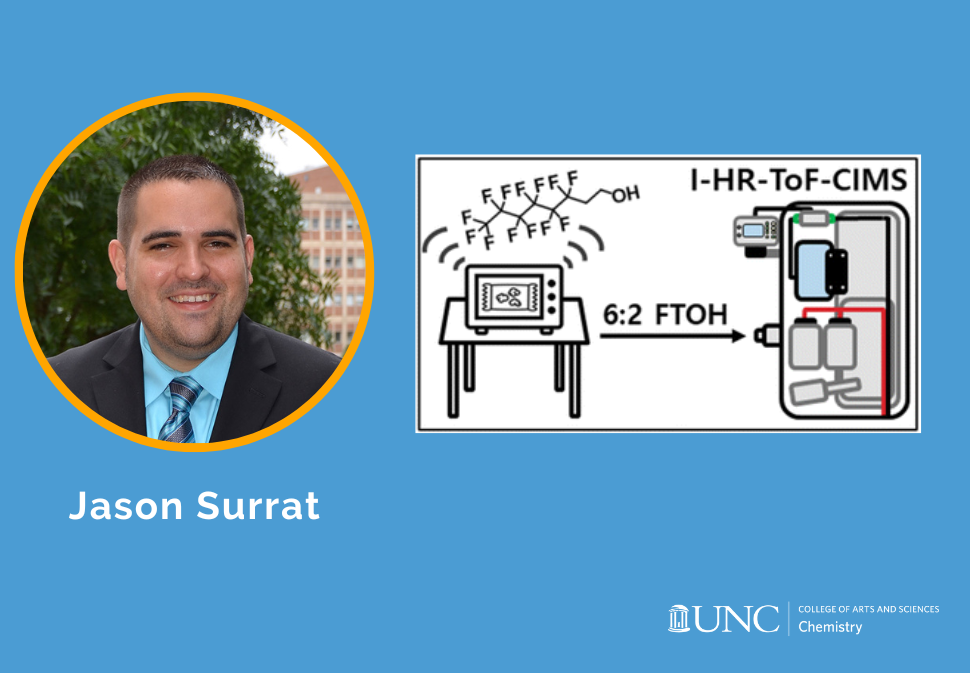
Herein, we present a direct liquid injection method for external calibration, providing detection limits of 0.19–3.1 pptv for 3 s averaging and 0.02–0.44 pptv for 120 s averaging, with the exception of E2, which had detection limits of 1700 and 220 pptv for 3- and 120 s averaging, respectively.

Amorphous glassy media composed of small molecular solutes or protein gels present general strategies for protecting against drying. We review these strategies and the proposed molecular mechanisms to explain protein protection in a vitreous matrix under conditions of low hydration.