Department News

In the study, “Evaluating Legacy and Emerging PFAS in Human Blood Collected from 2003 to 2021,” the UNC-led research team wanted to see whether PFAS exposure might be linked to autoimmunediseases.

The UNC-Chapel Hill Department of Chemistry is pleased to share that Megan Jackson, Assistant Professor of Chemistry, has been selected as a 2026 Cottrell Scholar by the Research Corporation for Science Advancement (RCSA).
Research

Herein, an approach for discriminating between tardigrade morphological states is developed and utilized to compare sucrose- and CaCl2-induced tuns, using the model species Hypsibius exemplaris.

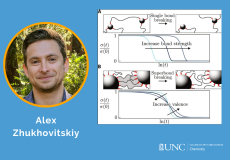
Herein, we disclose a backbone rearrangement approach to tune the short-chain branching of polymers.
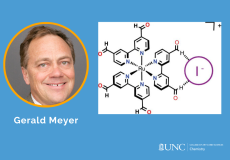
A new homoleptic Ru polypyridyl complex bearing two aldehyde groups on each bipyridine ligand, [Ru(dab)3](PF6)2, where dab is 4,4′-dicarbaldehyde-2,2′-bipyridine, was synthesized, characterized, and utilized for iodide photo-oxidation studies.
Our Faculty
Faculty in the Department of Chemistry at the University of North Carolina help define solutions to the pressing scientific problems of the day. A significant and key component of our department’s strategic plan is to cultivate the next generation of scientific leadership. Faculty, from our assistant professors to our most senior and distinguished colleagues, are international leaders in their subfields, garnering local, national, and international recognition and accolades commensurate with their excellence in research and teaching.
Our Graduate Students
Our graduate students form the next generation of scientific leaders. As a department, we seek to recruit and mentor a diverse cohort of students dedicated to excellence in the classroom and research laboratory. The creativity, drive, collegiality, and accomplishments of our graduate students in tackling difficult scientific problems are significant reasons why UNC is an international leader in chemical research.