Enhanced Ice Nucleation of Simulated Sea Salt Particles with the Addition of Anthropogenic Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances
Abstract
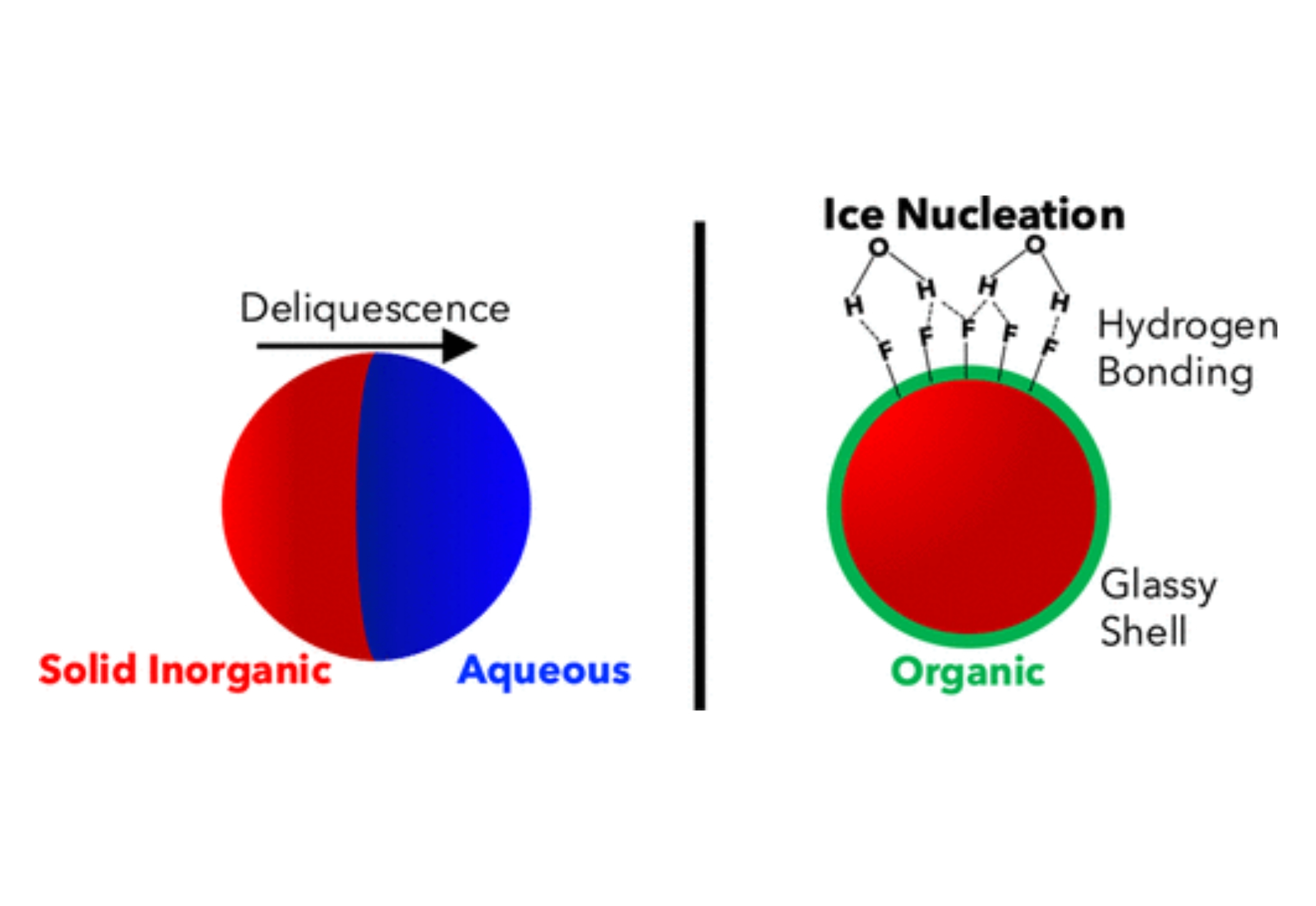
Ice-nucleating particles (INPs) impact global climate by altering cloud formation and properties. The ability of aerosol particles to nucleate ice is in part determined by particle composition. Here, we demonstrate that the addition of common fluorinated pollutants to seawater can enhance the ice nucleation activity of resulting simulated sea spray particles, although we note that ambient sea spray will have additional organic components not considered here. We quantified the ice supersaturation at the onset of ice nucleation, fractional INP activation, and ice nucleation active site density for inorganic sea salt, assemblages of per- and poly-fluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs), and internally mixed particles. Particles composed solely of PFASs or sea salt mixed with PFASs nucleated ice heterogeneously in a temperature (−50 ≤ T ≤ −40 °C) and ice supersaturation (1.0 ≤ Sice ≤ 1.5) range relevant to cirrus cloud formation. Conversely, the temperature and relative humidity trajectories considered here precluded heterogeneous ice nucleation of particles composed solely of inorganic sea salt. Our active site density calculations indicate that PFAS-containing sea salt aerosol exhibits ice nucleation activities similar to other effective INPs. Since the PFAS concentrations in our aerosolized solutions were similar to those observed in the ocean, our findings indicate that the addition of anthropogenic pollutants such as PFASs to seawater may enhance the ice-nucleating abilities of sea spray aerosols in the cirrus cloud regime. Further studies should investigate the interactions of PFASs with other marine organic matter to ascertain the impacts of particle composition on ambient sea spray’s ice nucleation activity.
Citation
Enhanced Ice Nucleation of Simulated Sea Salt Particles with the Addition of Anthropogenic Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances
Martin J. Wolf, Yue Zhang, Jiaqi Zhou, Jason D. Surratt, Barbara J. Turpin, and Daniel J. Cziczo
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry 2021 5 (8), 2074-2085
DOI: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.1c00138