A Permissive Amide N-Methyltransferase for Dithiolopyrrolones
Abstract
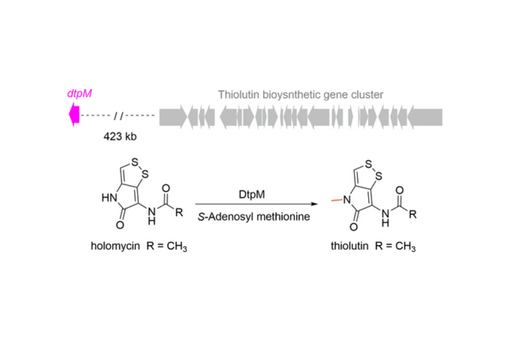
Amide N-methylation is important for the activity and permeability of bioactive compounds but can be challenging to perform selectively. The broad-spectrum antimicrobial natural products thiolutin and holomycin differ only by an N-methyl group at the endocyclic amide of thiolutin, but only thiolutin exhibits antifungal activity. The enzyme responsible for amide N-methylation in thiolutin biosynthesis has remained elusive. Here, we identified and characterized the amide N-methyltransferase DtpM that is encoded >400 kb outside of the thiolutin gene cluster. DtpM catalyzes efficient conversion of holomycin to thiolutin, exhibits broad substrate scope toward dithiolopyrrolones, and has high thermal stability. In addition, sequence similarity network analysis suggests DtpM is more closely related to phenol O-methyltransferases than some amide methyltransferases. This study expands the limited examples of amide N-methyltransferases and may facilitate chemoenzymatic synthesis of diverse dithiolopyrrolone compounds as potential therapeutics.
Citation
A Permissive Amide N-Methyltransferase for Dithiolopyrrolones
Xiaoyan Chen, Rachel M. Johnson, and Bo Li
ACS Catalysis 2023 13 (3), 1899-1905
DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.2c05439